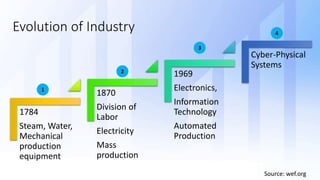
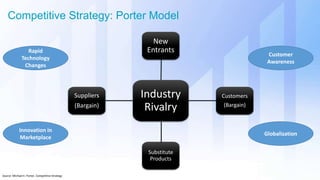
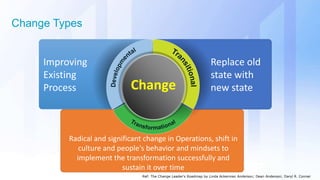
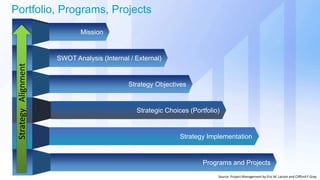
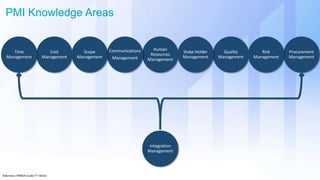
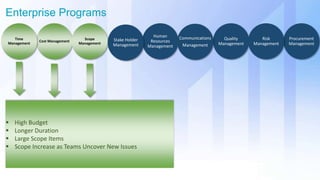
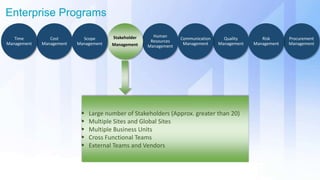
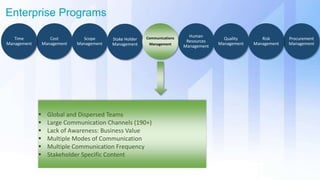
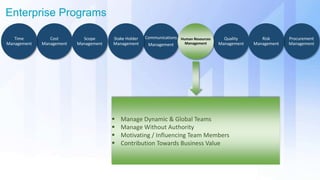
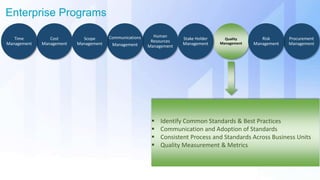
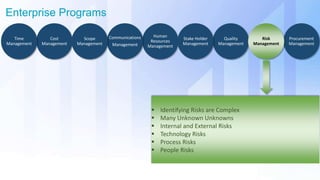
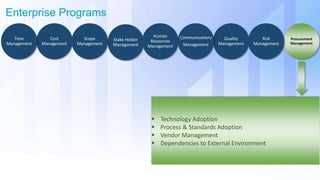
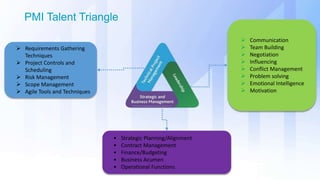
The document discusses skills needed to lead enterprise programs. It begins by covering the evolution of industry and disruptors like technology changes. It then discusses change management and different types of change. The rest of the document details skills across various areas like business, technical, and leadership that are important for leading large, complex enterprise programs. These include skills like communication, problem solving, emotional intelligence, strategic planning, and adapting to changing technologies. The key takeaway is to balance skills across business, technical and leadership domains and align program objectives to organizational strategy.