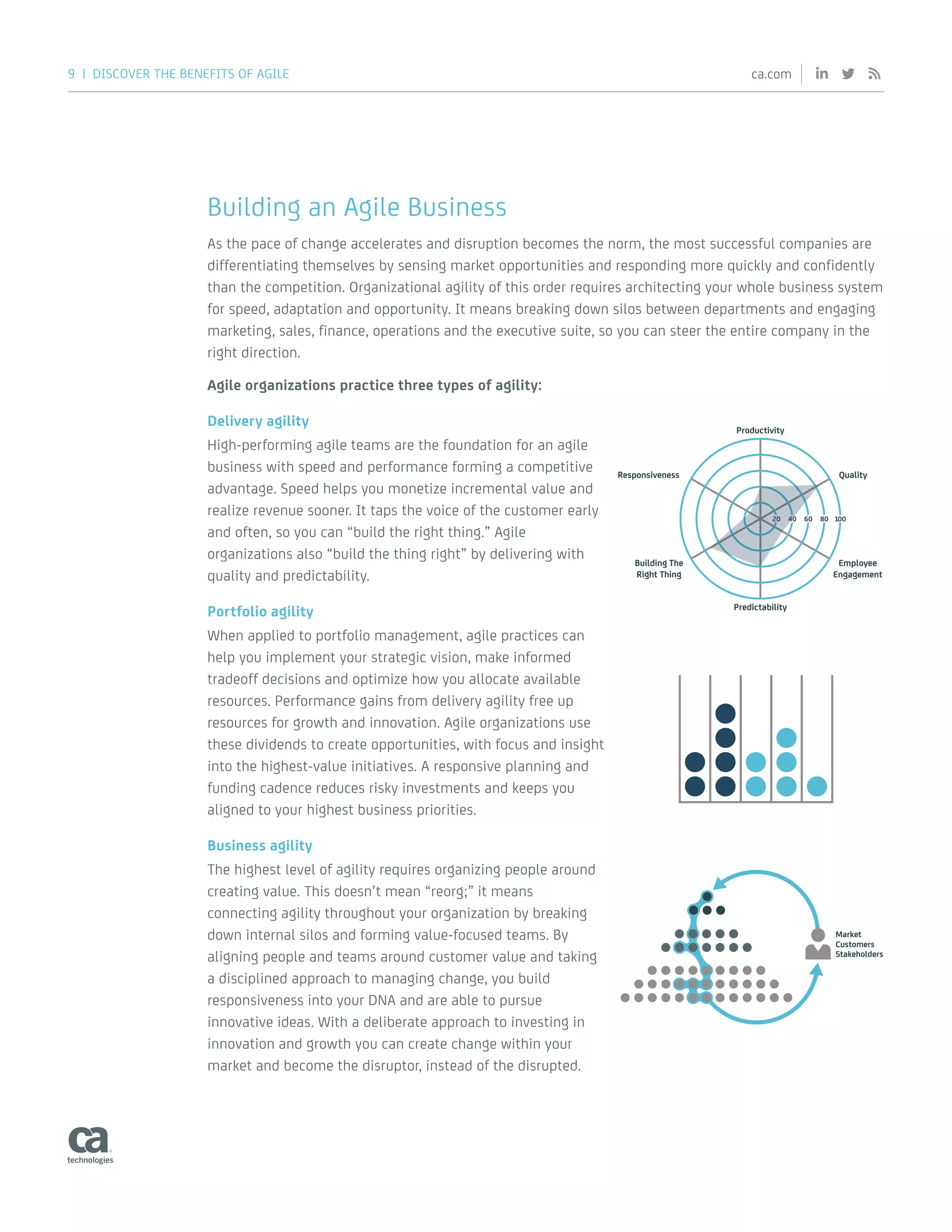
The document discusses the benefits of adopting an agile approach to software development and project management. Some key benefits mentioned include faster time to market, increased productivity, fewer defects, cost savings, and better employee engagement. Adopting agile approaches allows organizations to build high-quality products that customers value more quickly by delivering in short iterations and incorporating frequent customer feedback. It also helps reduce risks and eliminate waste compared to traditional sequential development methods. Successfully implementing agile requires changes not just to development teams but also to organizational structures, processes, and culture.