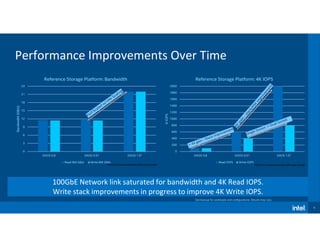
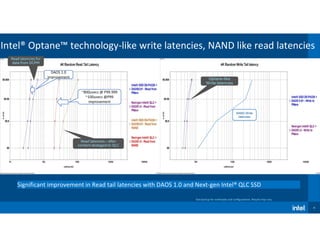
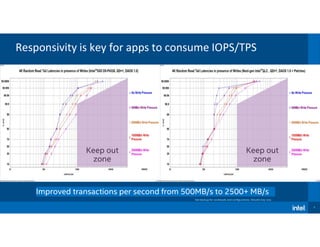
1) The document discusses the performance evolution of a reference storage platform over time as DAOS software improved from version 0.8 to 1.0.
2) Bandwidth and IOPS measurements increased significantly with each DAOS update as well as when using dual socket CPUs in DAOS 1.0.
3) Read latency times improved in DAOS 1.0, showing Optane-like write latencies and NAND-like read latencies from data destaged to QLC SSDs.