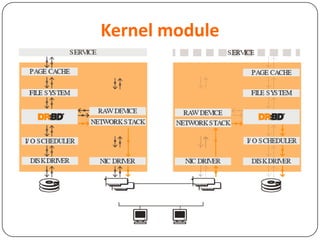
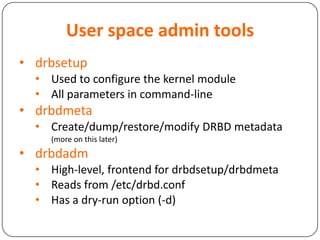
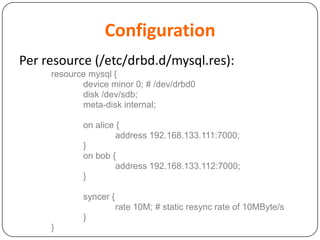
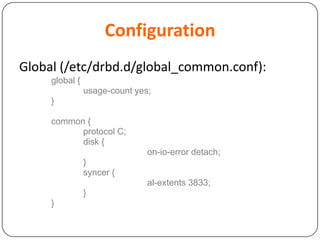
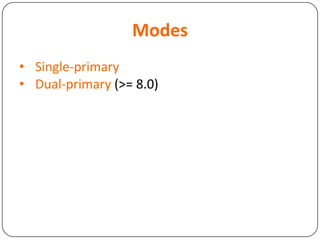
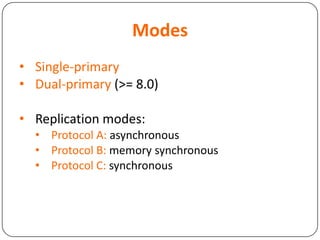
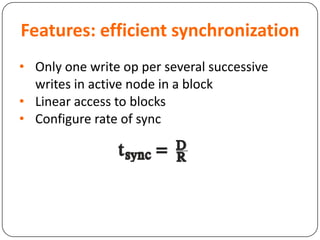
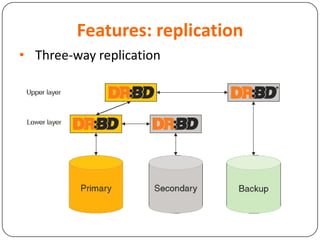
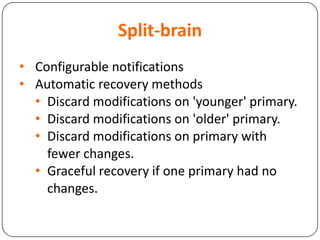
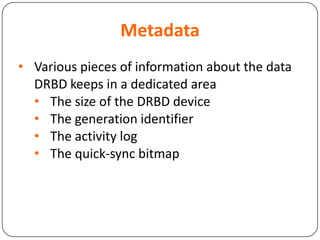
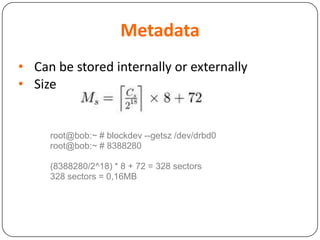
This document provides an overview of Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD), which is a software-based storage solution that mirrors the contents of block devices across multiple nodes in real-time. It describes DRBD's architecture including kernel modules, user space tools, resource configuration, roles, modes, features around efficient synchronization and data verification, and limitations.