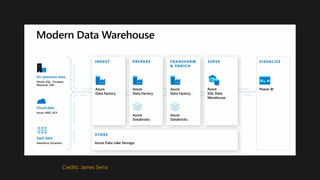
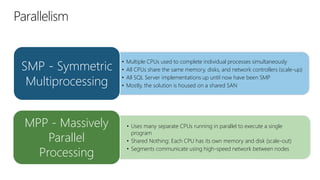
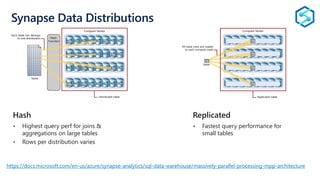
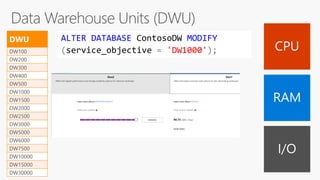
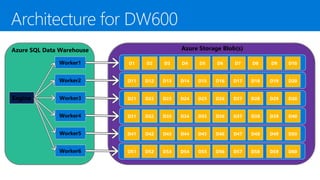
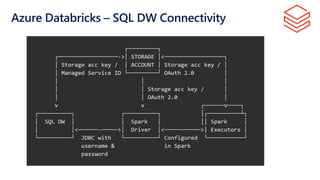
The document provides an overview of modern data warehousing using Azure's services, including features of Azure Data Lake Store (ADLS) and Azure Data Factory (ADF). It discusses the architecture of Azure Synapse Analytics, its massively parallel processing capabilities, and workloads suitable for SQL data warehousing. Additionally, it covers the differences between SQL Server and SQL Data Warehouse along with external data source integration and optimal use cases.