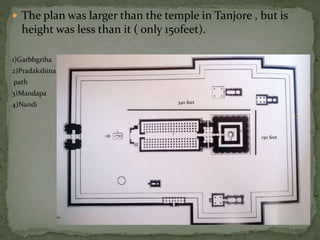
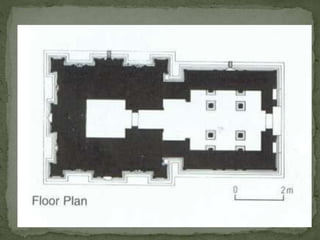
The document summarizes key architectural features of several South Indian temples from different periods. It describes:
1. The Srinivasanalur temple built during the reign of Parantaka I in the 10th century, which simplified Pallava elements and introduced changes like neck mouldings and kalasas.
2. Features adopted by later Dravidian style temples like the disappearance of lion motifs and inclusion of rakshasa heads.
3. Major temples like Brihadeeswarar at Tanjore and Gangaikondacholapuram that displayed the mature Chola style through their grand scale, intricate carvings, and tall pyramidal towers.