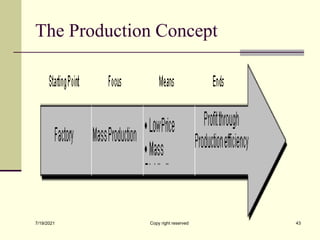
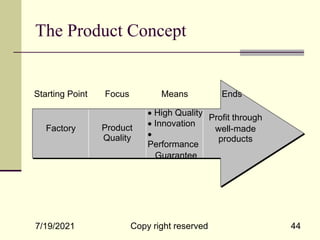
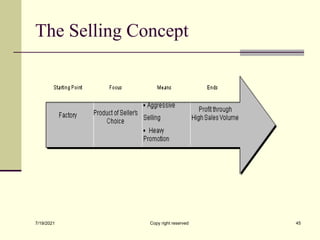
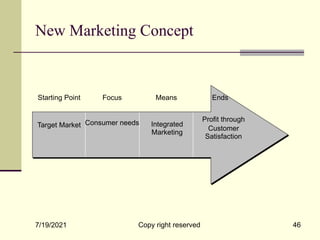
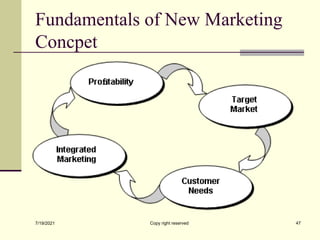
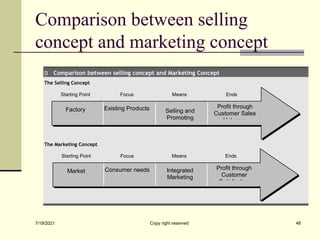
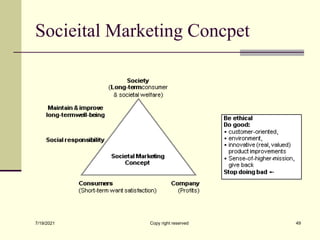
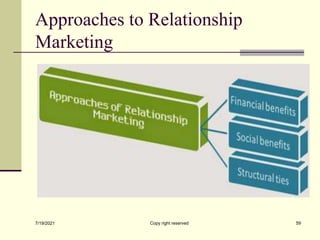
The document provides an overview of key marketing concepts including definitions of marketing from various sources. It discusses needs, wants and demand; products; value and customer satisfaction; exchange; distribution channels; markets; and the marketing environment. The document aims to introduce foundational marketing concepts and terms.