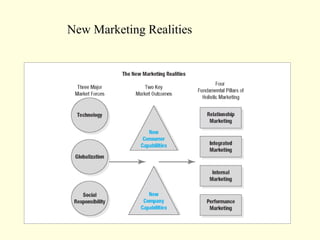
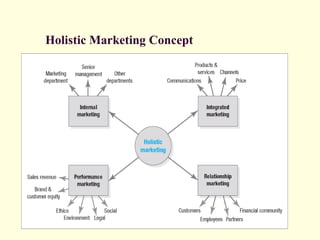
This document defines marketing for the 21st century. It discusses key marketing concepts such as needs, wants, demand, segmentation, targeting, positioning, products, brands, value, satisfaction, markets, exchange, channels, competition and environment. It notes the changing realities of technology, globalization and social responsibility. Marketing is defined as a social and managerial process to obtain what people need and want through creating and exchanging value. The document also discusses the evolution of marketing concepts over time and new frameworks such as focusing on people, processes, programs and performance, as well as key tasks for marketing management.