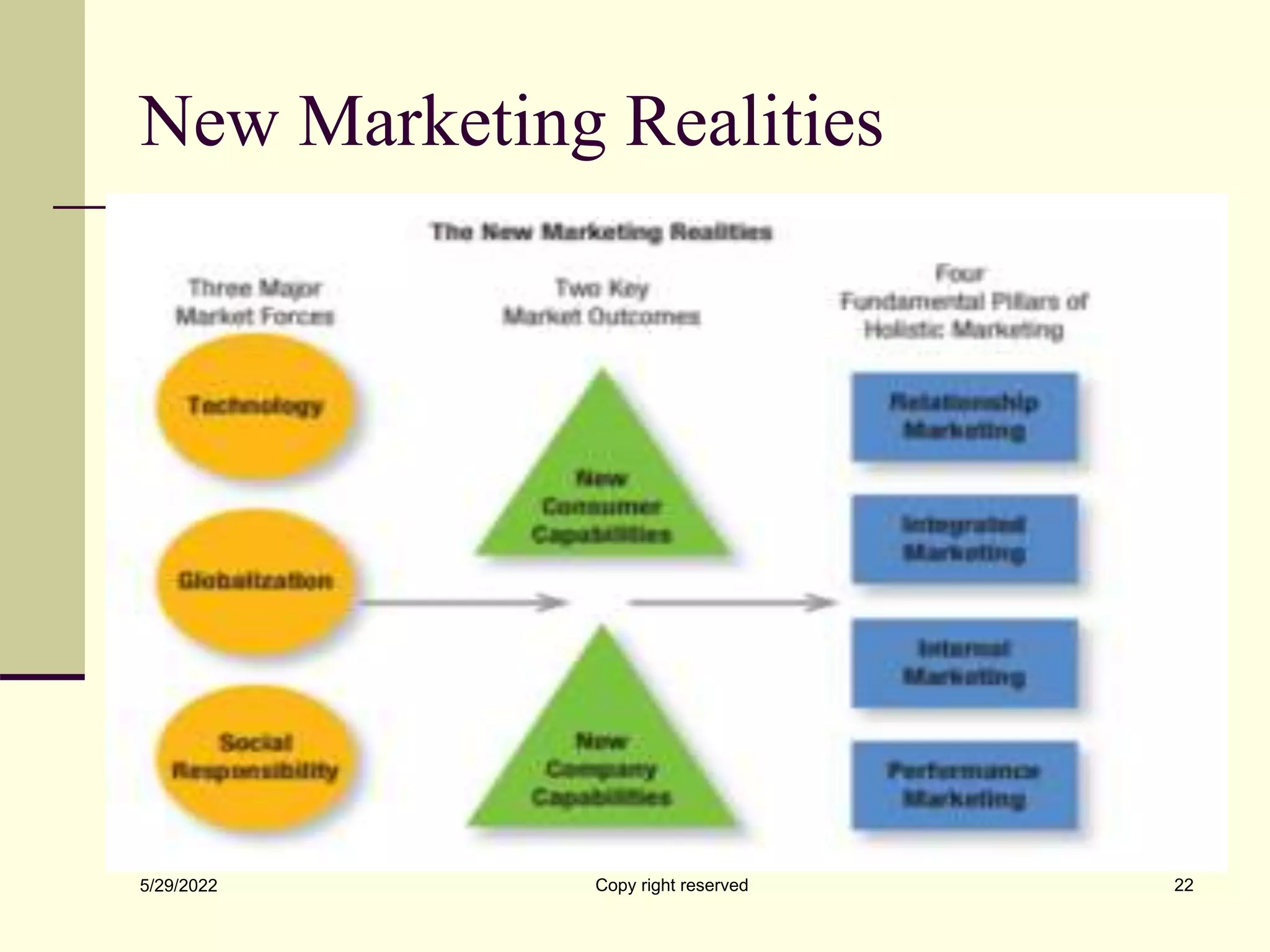
The document defines marketing and its key concepts. It discusses how marketing has evolved from a focus on production and selling to prioritizing customer needs and values. The document outlines traditional marketing mix elements like product, price, place and promotion as well as modern elements like people, process, programs and performance. It also discusses important marketing concepts such as segmentation, targeting, positioning, brands, and the relationship between customer benefits, costs and perceived value.