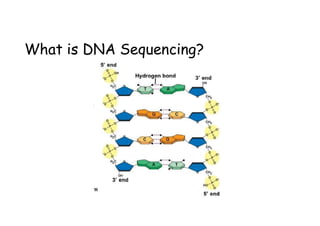
DNA sequencing involves determining the order of nucleotides in DNA. The Sanger method is commonly used and involves DNA polymerase, dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) which terminate DNA strand elongation, and fluorescent dyes. Modern sequencing uses capillary electrophoresis to separate the terminated strands by size and a CCD camera detects the fluorescent dyes to determine the sequence. High-throughput sequencing utilizes multiple capillaries to process many samples simultaneously.