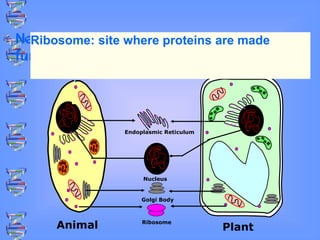
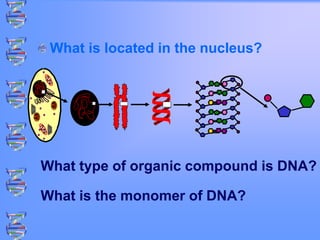
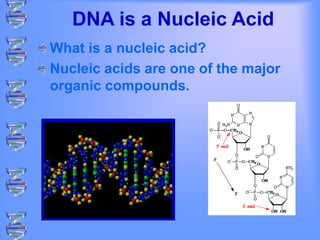
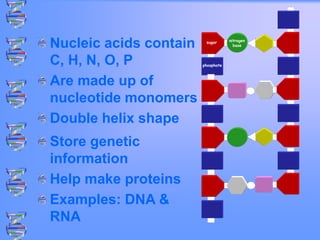
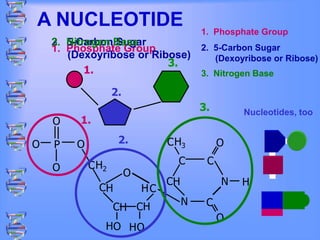
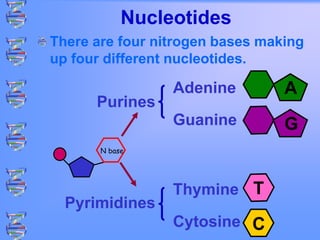
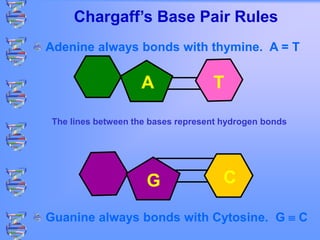
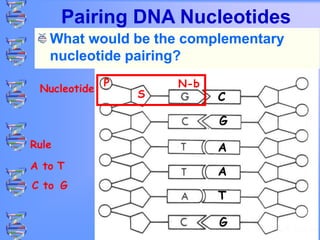
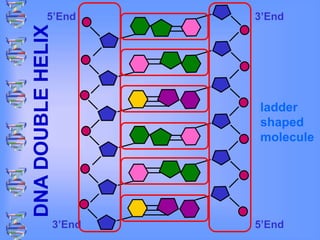
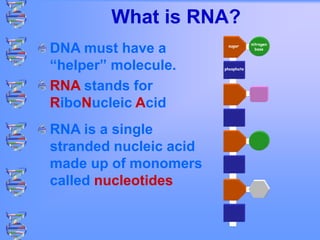
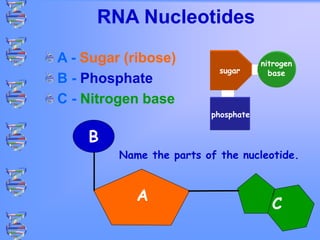
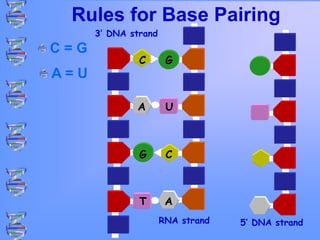
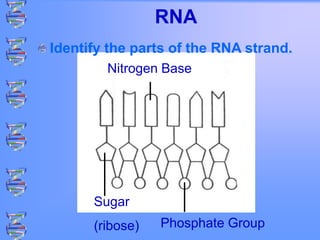
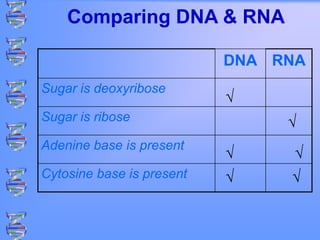
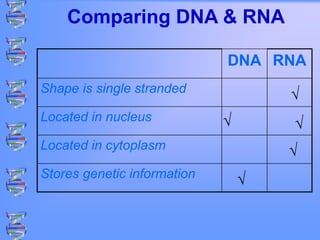
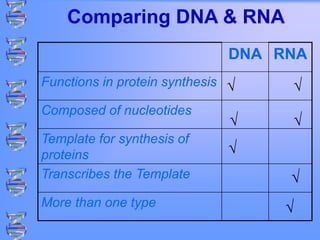
The document discusses DNA and RNA. It defines DNA as a double-stranded nucleic acid located in the nucleus that stores genetic information through base pairing of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid that carries DNA's message to help synthesize proteins, comes in different types like mRNA and tRNA, and contains the nucleotide uracil instead of thymine. The document compares the key differences and similarities between DNA and RNA.