The document provides information about an industrial training report submitted by MD. Shadab for their Bachelor of Technology degree in Civil Engineering. It includes details about the company J. Kumar & CRTG Joint Venture where the training took place, working on the Delhi Metro Rail Project Phase-III underground construction. Key points:
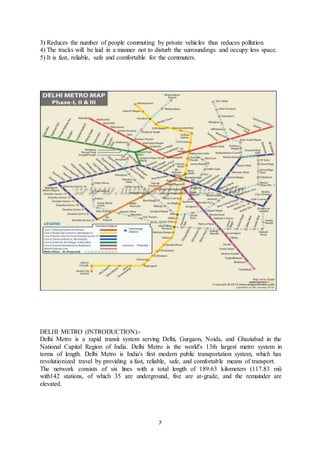
(a) The report describes MD. Shadab's industrial training working on the Delhi Metro Rail Project Phase-III underground construction from July 10th to August 10th 2017 under the supervision of J. Kumar & CRTG Joint Venture.
(b) It includes details about the companies involved in the project like J. Kumar, CRTG, and DMRC, as well