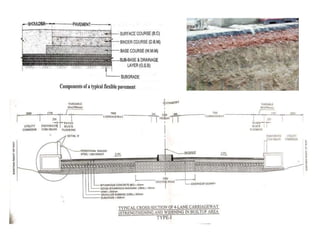
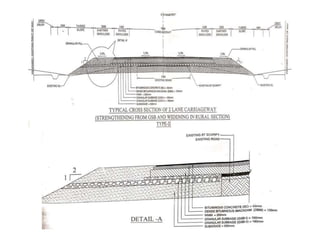
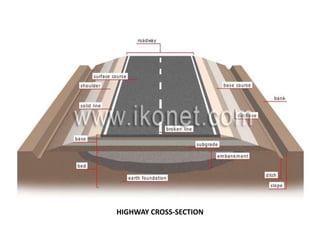
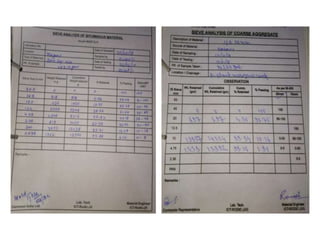
The document provides details of Amit Kumar's 45-day industrial/vocational training report on the rehabilitation and upgradation of the Maheshkhut-Saharsha-Purnea section of National Highway 107 in Bihar. The training was conducted with National Highways Authority of India and Gammon Engineers & Contractors Pvt. Ltd. as part of Amit's civil engineering degree. The report describes the various steps involved in highway construction including planning, surveying, execution through grading, embankment construction, subgrade preparation, and paving layers. It also discusses quality control procedures and safety measures implemented at the construction site.