DLL in Math 7 Week 4.docx
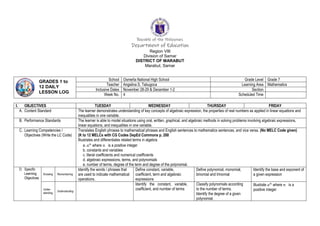
- 1. Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samar DISTRICT OF MARABUT Marabut, Samar GRADES 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School Osmeña National High School Grade Level Grade 7 Teacher Angelina S. Tabugoca Learning Area Mathematics Inclusive Dates November 28-29 & December 1-2 Section Week No. 4 Scheduled Time I. OBJECTIVES TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY A. Content Standard The learner demonstrates understanding of key concepts of algebraic expression, the properties of real numbers as applied in linear equations and inequalities in one variable. B. Performance Standards The learner is able to model situations using oral, written, graphical, and algebraic methods in solving problems involving algebraic expressions, linear equations, and inequalities in one variable. C. Learning Competencies / Objectives (Write the LC Code) Translates English phrases to mathematical phrases and English sentences to mathematics sentences, and vice versa. (No MELC Code given) (K to 12 MELCs with CG Codes DepEd Commons p. 288 Illustrates and differentiates related terms in algebra: a. 𝑎𝑛 where 𝑛 is a positive integer b. constants and variables c. literal coefficients and numerical coefficients d. algebraic expressions, terms, and polynomials e. number of terms, degree of the term and degree of the polynomial. D. Specific Learning Objectives Knowing Remembering Identify the words / phrases that are used to indicate mathematical operations. Define constant, variable, coefficient, term and algebraic expressions Define polynomial, monomial, binomial and trinomial Identify the base and exponent of a given expression Under- standing Understanding Identify the constant, variable, coefficient, and number of terms Classify polynomials according to the number of terms. Identify the degree of a given polynomial. Illustrate 𝑎𝑛 where 𝑛 is a positive integer
- 2. Applying Translate verbal phrases to mathematical phrases and vice versa. Analyzing Illustrate and differentiate terms related to Algebra Evaluating Evaluate an. Doing Creating Integration Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding II. CONTENT Verbal Phrases and Mathematical Phrases Algebraic Expressions (Constants, Variables, Coefficients, and Terms) Classifying Polynomials Laws of Exponents III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learners’ Materials pages pp. 117 – 121 pp.126 - 129 pp.126 - 129 3. Textbook pages Orlando A. Oronce and Marilyn O. Mendoza e-math, Worktext in Mathematics 7 pp. 166-168 Gladys C. Nivera, Making Connections in Mathematics I pp. 99 – 104 Orlando A. Oronce and Marilyn O. Mendoza e-math, Worktext in Mathematics 7 pp. 177-182 Gladys C. Nivera, Making Connections in Mathematics I pp. 99 – 104 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resources Portals B. Other Learning Resources https://www.palmbeachstate.edu/prepmathlw/ Documents/translatingkeywords.pdf IV. PROCEDURES A. Revisiting previous lesson or presenting the new lesson Review on constant and variable. Review on translating verbal phrases to mathematical phrases and vice versa Review on constant, variable, coefficient, term, and algebraic expressions Review on polynomials Pre-Assessment Give the product of each of the following as fast as you can. a) 3 x 3 = ________ b) 4 x 4 x 4 = ________ c) 5 x 5 x 5 = ________ d) 2 x 2 x 2 = ________ e) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = _______ f) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 =______ B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson Present the topic and its objectives: Identify the words / phrases that are used to indicate mathematical operations. Present the topic and its objectives: Define constant, variable, coefficient, term and algebraic expressions Present the topic and its objectives: Define polynomial, monomial, binomial and trinomial Present the topic and its objectives: Identify the base and exponent of a given expression
- 3. Translate verbal phrases to mathematical phrases and vice versa. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Identify the constant, variable, coefficient, and number of terms Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Classify polynomials according to the number of terms. Identify the degree of a given polynomial. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding. Illustrate 𝑎𝑛 where 𝑛 is a positive integer Evaluate an. Value accumulated knowledge as means of new understanding C. Presenting examples/ instances of the new lesson Given a series of examples, let the students define the following: 1. constant 2. variable 3. coefficient 4. term 5. algebraic expressions Define the following terms by giving examples: 1. monomial 2. binomial 3. trinomial 4. degree of a monomial 5. degree of a polynomial Define the following: 1. base 2. exponent
- 4. D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 TRANSLATING KEY WORDS AND PHRASES INTO ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS The table above lists some key words and phrases that are used to describe common mathematical operations. Examples of Algebraic expressions: −4, 𝑥, 2𝑥𝑦3 , −4𝑚, 𝑚 − 2, 2𝑥3 + 3𝑥 − 2 Consider the following: Discuss this example thoroughly by illustrating and differentiating terms related to algebra. Present the procedure in identifying or classifying polynomials: a. Look for plus or minus signs separating the terms. (Although we defined a polynomial as a sum of one or more terms, any one of those could be a negative term.) b. Make sure that there are no variables in the denominator of any of the terms, nor any variable under the radical sign) c. Count the number of terms and name the expressions accordingly. Use the pre-assessment as the springboard in defining base and exponent. Give the product of each of the following as fast as you can. a) 3 x 3 = ________ b) 4 x 4 x 4 = ________ c) 5 x 5 x 5 = ________ d) 2 x 2 x 2 = ________ e) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = _______ f) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 =______ Based on the above example, express each item in terms of base and exponent. a) 32 b) 43 c) 53 d) 23 e) 24 f) 25 E. Discussing concepts and practicing new skills #2 Present the following examples to the students and let them understand how translation is done. Activity: Identify Me1! Directions: Identify the constants, variables, numerical coefficient, literal coefficient, and terms in each algebraic expression. A. Identify the following polynomials: 1. 4𝑥2 𝑦3 2. 𝑥2 − 10 3. −30 4. 3𝑥4 − 5𝑥 + 8 Rewrite each of these in exponential form. (an) a) 5∙5∙5∙5∙5 = ______ b) (a)(a)(a)(a) = ______ c) 6∙x∙x∙x∙x∙x∙x= ______ d) 7∙7∙y∙y = ______ e) 10 = ______
- 5. Verbal Phrase Algebraic Translation the product of 8 and m 8m 10 times c 10c twice x 2x ½ of p 1/2p 7 multiplied by b 7b the quotient of 8 and m 8/m 10 divided by c 10/c The ratio of 7 to a 7/a P split into 4 equal parts p/4 X divided by into 10 10/x 10 divided into q q/10 5. 2𝑎3 + 𝑏𝑐 𝑎 B. Identify the degree of each polynomial. 1. 2𝑎3 𝑏2 𝑐 + 5 2. 10𝑥5 − 8𝑥3 + 8𝑥 + 4 F. Developing mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) A. Let the students translate the following by writing at least two verbal phrases for each expression: 1. 8-3 2. n + 5 3. 2+𝑛 3 4. 3+𝑛 4 B. Let 𝑛 a certain number. Then translate each into an algebraic expression. 1. 9 more than a number 2. 14 decreased by a number 3. 12 more than 5 times a number Activity: Identify Me2! Directions: Identify the constants, variables, numerical coefficient, literal coefficient, and terms in each algebraic expression. Classify and identify each of the following polynomials as to number of terms and degree. A. Express the following in exponential from and find the value of the expression: 1. 3⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 2. 7⋅7⋅7 3. z⋅z⋅z⋅z⋅z 4. 4⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 5. (2x)(2x)(2x)
- 6. 4. a number divided by 7 5. 2 raised to a number G. Finding practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living Group Activity H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson In translating verbal phrases into mathematical phrases, consider the following terms: Addition would indicate an increase, a putting together, or combining. Thus, phrases like increased by and added to are addition phrases. Subtraction would indicate a lessening, diminishing action. Thus, phrases like decreased by, less, diminished by are subtraction phrases. Multiplication would indicate a multiplying action. Phrases like multiplied by or times are multiplication phrases. Division would indicate partitioning, a quotient, and a Algebraic Expressions is a statement containing one or more terms connected by plus or minus signs. A term (algebraic term) is a number, variable, or a product or quotient of numbers and variables. A variable is a symbol (usually letter/letters) used to represent an unknown quantity (number). A constant is a single number or a number, letter, or symbol which value is fixed. Numerical Coefficient is the number in an algebraic term. Classifying Polynomials based on the Number of Terms 1. A polynomial with one term is called a monomial 2. A polynomial with two terms is called a binomial 3. A polynomial with three terms is called a trinomial Degree: The degree of a monomial is the total number of times its variable occurs as factors The degree of a polynomial is the greatest of the degree of its term The exponent tells us how many times the base is multiplied by itself. The base is the factor which is to be multiplied by itself n times to obtain the product. The power refers to the product of equal factors. To interpret an where n is a positive integer: an= a x a x a x a ….. (n times) *a is called the base *n is called the exponent Ex. 53 = 5x5x5 = 125
- 7. ratio. Phrases such as divided by, ratio of and quotient of are common for division. Literal Coefficient is a letter used to represent a number. Polynomial is an algebraic expression that represents a sum of one or more terms containing whole number exponents on the variables. I. Evaluating learning Directions: Translate the given verbal phrases into mathematical expressions or vice versa. a) The sum of a number and three b) Four times a certain number decreased by one c) The ratio of a number x and six increased by two d) A certain number decreased by two e) The product of p and q divided by three f) 9m g) 4x– 7 h) 5(x+1) i) 4 + x j) 2a + 3 Directions: Identify the constants, variables, numerical coefficient, literal coefficient, and terms in each algebraic expression. Classify and identify each of the following polynomials as to number of terms and degree. Identify the base and the exponent. Then evaluate the expression. a) 28 b) 82 c) 51 d) 32 e) 182 J. Additional activities for application or remediation 1. Follow-up: Write your own pair of mathematical phrase and its verbal translation. 2. Study: Polynomials Define the following: 1. Monomial 2. Binomial 3. Trinomial 1. Follow-up Activity: Rewrite in exponential form: a)(xyz)(xyz)(xyz) b)3∙3∙3∙x∙x∙y∙y∙y 2. Study: Laws of Exponent pages 126-129 (Learner’s Material) V. REMARKS REFLECTION
- 8. VI. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation. A. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation B. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson. C. No. of learners who continue to require remediation. D. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did it work? E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did it work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other learners? Prepared by: ANGELINA S. TABUGOCA Teacher III Reviewed by: GLENDA G. SEBANDAL. MT-I, Department Head – Designate Noted: CONCEPCION P. MABINI Secondary School Principal IV