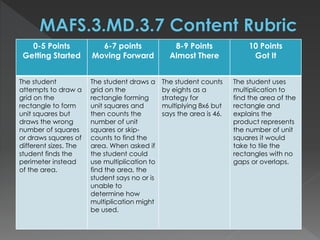
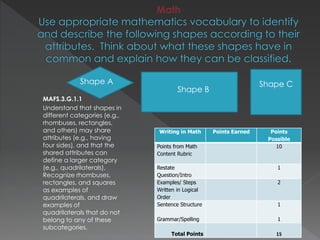
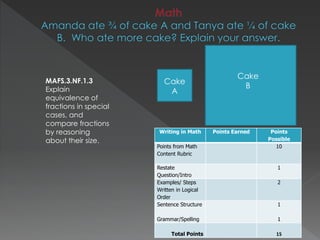
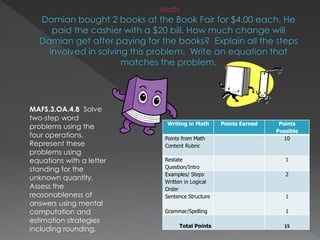
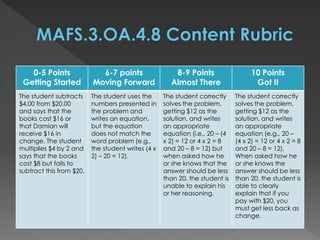
The document contains standards and learning targets for 3rd grade science and math. It includes standards about properties of matter, characteristics of plants, measurement of time and length, and fractions. It also provides examples of student work and rubrics to assess understanding of area, geometry, time telling, and multi-step word problems.