This document discusses different number systems used in computer architecture including binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. It provides examples of converting between these number systems, such as converting the decimal number 47 to binary (101111), octal (57), and hexadecimal (2F). Conversion charts and formulas are provided for changing between the number systems.



![Number systems [Binary ]
A Binary number system has only two digits that are 0 and 1. Every number
(value) represents with 0 and 1 in this number system. The base of binary
number system is 2, because it has only two digits
4
0 , 1
1 ≥ ≥ 𝟎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-4-2048.jpg)
![Number systems [Octal]
1. Octal number system has only eight (8) digits from 0 to 7.
2. The base of octal number system is 8, because it has only 8 digits.
5
0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7
7 ≥ ≥ 𝟎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-5-2048.jpg)
![Number systems [Decimal]
1. Decimal number system has only ten (10) digits from 0 to 9.
2. The base of decimal number system is 10, because it has only 10 digits.
6
0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9
9 ≥ ≥ 𝟎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-6-2048.jpg)
![Number systems [Hexadecimal]
1. A Hexadecimal number system has sixteen (16) alphanumeric values
from 0 to 9 and A to F.
2. The base of hexadecimal number system is 16, because it has 16
alphanumeric values. Here A is 10, B is 11, C is 12, D is 13, E is
14 and F is 15.
7
0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , A , B , C , D , E , F
F ≥ ≥ 𝟎](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-7-2048.jpg)
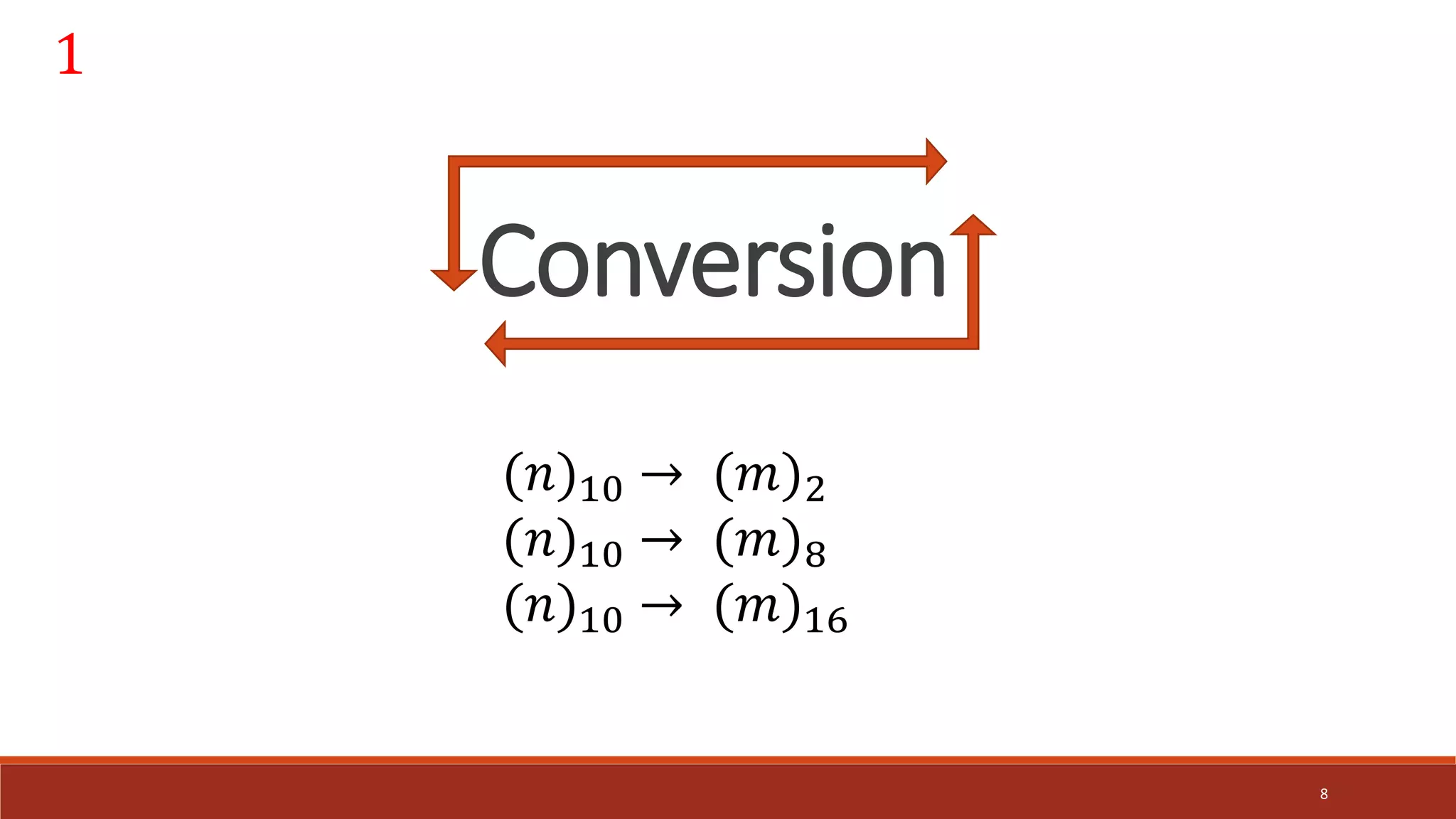
![Convert Decimal to [ Binary ]
9
(47)10 = (101111)2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-9-2048.jpg)
![Convert Decimal to [ Octal ]
10
(47)10 = (57)8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-10-2048.jpg)
![Convert Decimal to [hexadecimal ]
11
(47)10 = (2𝐹)16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-11-2048.jpg)

![Convert Binary to [Decimal ]
13
(101111)2 = (47)10
101111 2 ⇒ 1 ∗ 25
+ 0 ∗ 24
+ 1 ∗ 23
+ 1 ∗ 22
+ 1 ∗ 21
+ 1 ∗ 20
⇒ 32 + 0 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-13-2048.jpg)
![Convert Binary to [Octal ]
14
(101111)2 = (57)8
101111 2 ⇒ 1 ∗ 25 + 0 ∗ 24 + 1 ∗ 23 + 1 ∗ 22 + 1 ∗ 21 + 1 ∗ 20
⇒ 32 + 0 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-14-2048.jpg)
![Convert Binary to [hexadecimal]
15
(101111)2 = (2𝐹)16
101111 2 ⇒ 1 ∗ 25 + 0 ∗ 24 + 1 ∗ 23 + 1 ∗ 22 + 1 ∗ 21 + 1 ∗ 20
⇒ 32 + 0 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-15-2048.jpg)

![Convert Octal to [Decimal]
17
(57)8 = (47)10
57 8 ⇒ 5 ∗ 81
+ 7 ∗ 80
⇒ 40 + 7
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-17-2048.jpg)
![Convert Octal to [Binary]
18
(57)8 = (101111)2
57 8 ⇒ 5 ∗ 81 + 7 ∗ 80
⇒ 40 + 7
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-18-2048.jpg)
![Convert Octal to [hexadecimal]
19
(57)8 = (2𝐹)16
57 8 ⇒ 5 ∗ 81 + 7 ∗ 80
⇒ 40 + 7
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-19-2048.jpg)

![Convert hexadecimal to [decimal]
21
(2𝐹)16 = (47)10
2𝐹 16 ⇒ 2 ∗ 161 + 𝐹 ∗ 160
⇒ 32 + 15
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-21-2048.jpg)
![Convert hexadecimal to [decimal]
22
(2𝐹)16 = (57)8
2𝐹 16 ⇒ 2 ∗ 161 + 𝐹 ∗ 160
⇒ 32 + 15
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-22-2048.jpg)
![Convert hexadecimal to [binary]
23
(2𝐹)16 = (101111)2
2𝐹 16 ⇒ 2 ∗ 161 + 𝐹 ∗ 160
⇒ 32 + 15
⇒ (47)10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dld-2-220313070425/75/Dld-2-23-2048.jpg)

