This document contains an exercise on digital electronics concepts including:
1. The differences between analog and digital measurements and pros and cons of analog vs digital electronics.
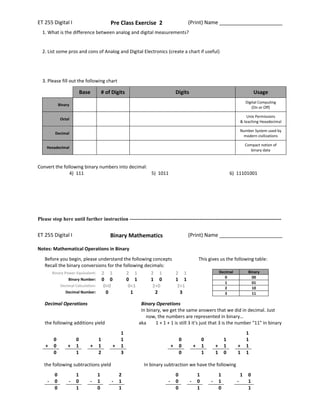
2. Tables defining binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal number systems.
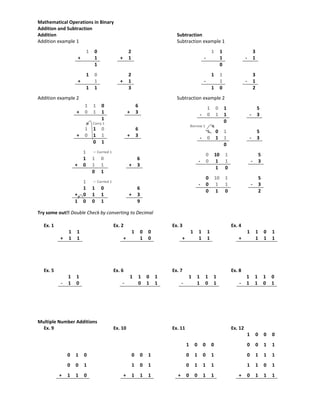
3. Practice problems converting between number systems and performing basic binary math operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
4. An independent practice section with additional problems converting between number systems and performing binary math.