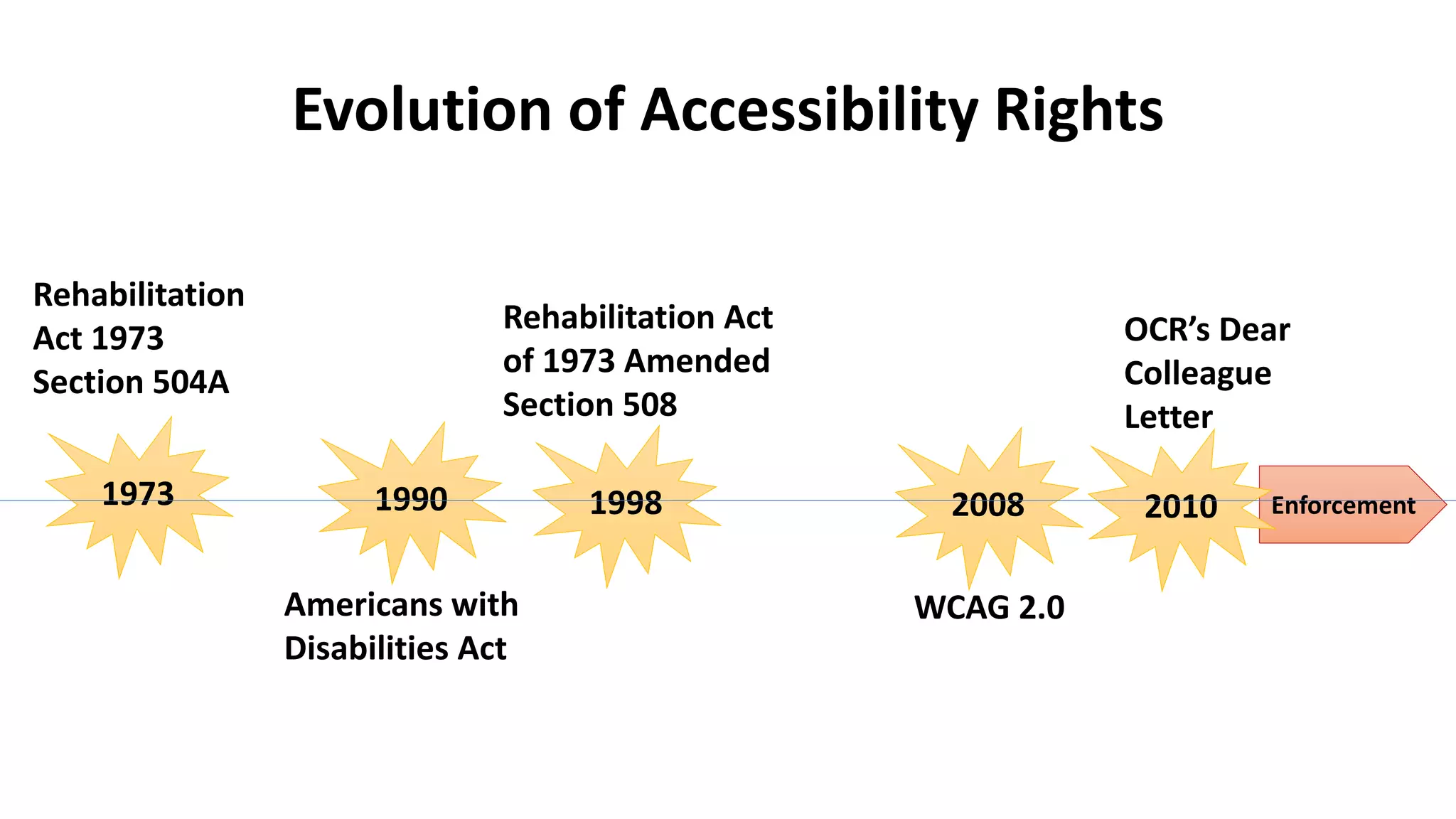
The document discusses issues of accessibility and universal design for learning in digital education, outlining key concepts such as the Americans with Disabilities Act, Section 504, and the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. It also provides recommendations for making online courses and websites accessible to students with disabilities through practices like using alternative text for images, captioning videos, and ensuring color selection does not impede those with color blindness. The document is presented by Raymond Rose and contains contact information for accessibility certification courses through the Texas Distance Learning Association.