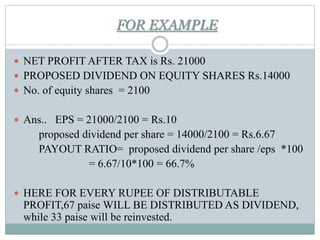
The dividend payout ratio measures the percentage of a company's net earnings that are paid out in dividends. It is calculated by dividing the total dividend amount by the net income. A lower payout ratio indicates that more earnings are being retained for reinvestment, while a higher ratio means more earnings are being distributed to shareholders. The payout ratio is important for investors to consider because it provides information about how much cash a company is willing to pay out versus reinvesting for future growth.