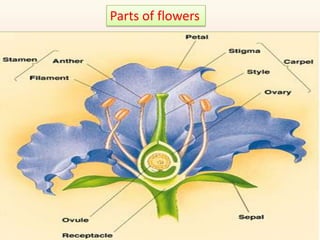
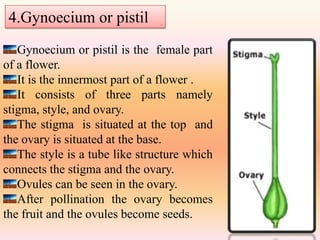
The document discusses the diversity of flower structures. It describes the main parts of flowers - calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. The calyx is the outermost structure that protects the flower bud. The corolla contains colorful petals that attract pollinators. The androecium contains stamens that produce and release pollen. The gynoecium or pistil contains the female parts. Flowers can be bisexual if they contain both male and female parts, or unisexual if they only contain one. Flowers also vary in their symmetry, from radially symmetrical to bilaterally symmetrical to asymmetrical. Diagrams of whole flowers, half