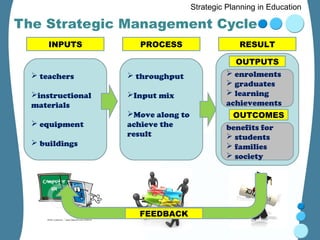
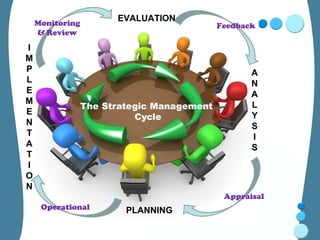
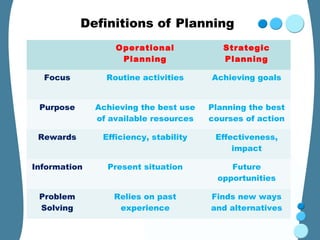
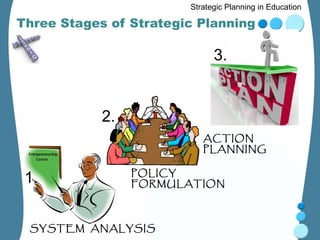
Strategic planning in education involves three key stages: 1) System analysis which examines how the education system functions internally and externally. 2) Policy formulation which identifies strategic goals and methods based on issues identified. 3) Action planning which translates policies into specific, measurable actions including objectives, strategies, responsibilities and timelines. The strategic planning process helps ensure resources are used effectively to achieve educational goals and benefits for students, families and society.