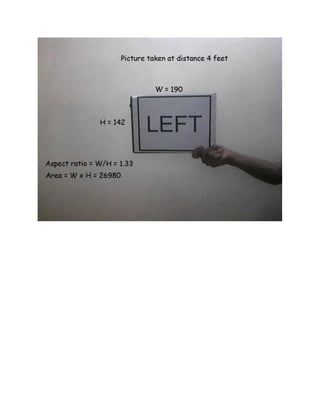
This document describes a distance measuring algorithm using a single camera. It has three parts: track the object using its aspect ratio, feed set points of known distances and areas into a table, and apply Lagrange's interpolation formula to the data to calculate distances based on measured areas. The algorithm tracks objects by finding those with an aspect ratio of around 1.3, and uses five sample points of distance and corresponding areas to determine distance for any given measured area value. A limitation is that the method does not work if the camera moves too close to the object.