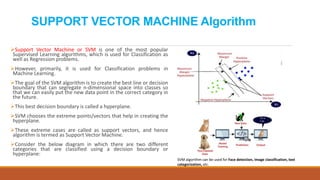
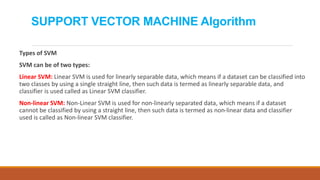
The document discusses linear and non-linear support vector machine (SVM) algorithms. SVM finds the optimal hyperplane that separates classes with the maximum margin. For linear data, the hyperplane is a straight line, while for non-linear data it is a higher dimensional surface. The data points closest to the hyperplane that determine its position are called support vectors. Non-linear SVM handles non-linear separable data by projecting it into a higher dimension where it may become linearly separable.

![LEAST SQUARES METHODS
The least square method is the process of finding the best-fitting
curve or line of best fit for a set of data points by reducing the sum of
the squares of the offsets (residual part) of the points from the curve
also called regression line.
During the process of finding the relation between two variables,
the trend of outcomes are estimated quantitatively. This process is
termed as regression analysis.
Least square method is the process of finding a regression line or
best-fitted line for any data set that is described by an equation.
Our main objective in this method is to reduce the sum of the
squares of errors as much as possible. This is the reason this method
is called the least-squares method.
This method is often used in data fitting where the best fit result is
assumed to reduce the sum of squared errors that is considered to
be the difference between the observed values and corresponding
fitted value.
Fig: Least squares method example [1]
[1] https://www.cuemath.com/data/least-squares/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3pyag3rrcouwno5mfhgw-chapter-2-230328120038-b6fb32ee/85/MSE-pptx-2-320.jpg)



![LEAST SQUARES METHODS
(Least Square Method Example)
Substituting these values in the normal equations,
10a + 62b = 72….(1)
62a + 468b = 503….(2)
(1) × 62 – (2) × 10,
620a + 3844b – (620a + 4680b) = 4464 – 5030
-836b = -566
b = 566/836
b = 283/418
b = 0.677
Substituting b = 0.677 in equation (1),
10a + 62(0.677) = 72
10a + 41.974 = 72
10a = 72 – 41.974
10a = 30.026
a = 30.026/10
a = 3.0026
Therefore, the equation becomes,
y = a + bx
y = 3.0026 + 0.677x Fig. This is the required trend line
equation.
Now, we can find the sum of squares of deviations
from the obtained values as:
d1 = [4 – (3.0026 + 0.677*8)] = (-4.4186)
d2 = [12 – (3.0026 + 0.677*3)] = (6.9664)
d3 = [1 – (3.0026 + 0.677*2)] = (-3.3566)
d4 = [12 – (3.0026 + 0.677*10)] = (2.2274)
d5 = [9 – (3.0026 + 0.677*11)] =(-1.4496)
d6 = [4 – (3.0026 + 0.677*3)] = (-1.0336)
d7 = [9 – (3.0026 + 0.677*6)] = (1.9354)
d8 = [6 – (3.0026 + 0.677*5)] = (-0.3876)
d9 = [1 – (3.0026 + 0.677*6)] = (-6.0646)
d10 = [14 – (3.0026 + 0.677*8)] = (5.5814)
∑d2 = (-4.4186)2 + (6.9664)2 + (-3.3566)2 + (2.2274)2 + (-
1.4496)2 + (-1.0336)2 + (1.9354)2 + (-0.3876)2 + (-
6.0646)2 + (5.5814)2 = 159.27990](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3pyag3rrcouwno5mfhgw-chapter-2-230328120038-b6fb32ee/85/MSE-pptx-6-320.jpg)