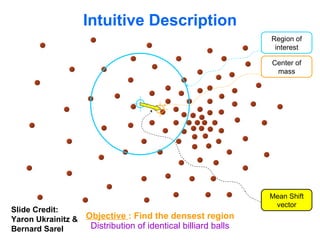
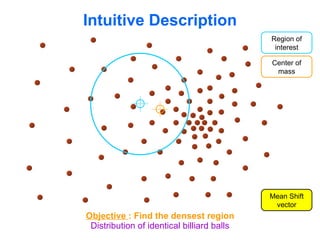
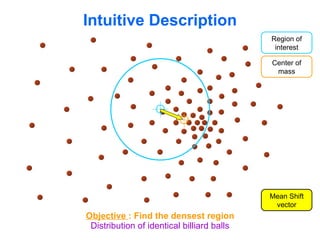
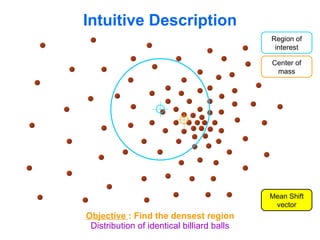
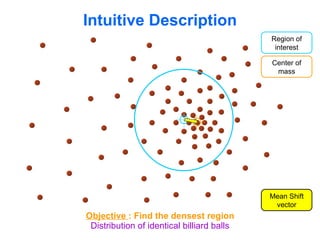
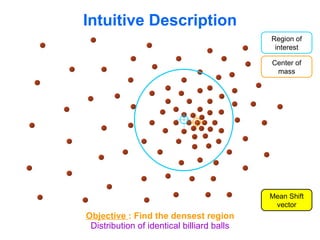
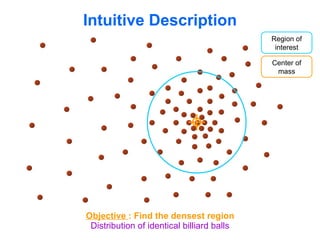
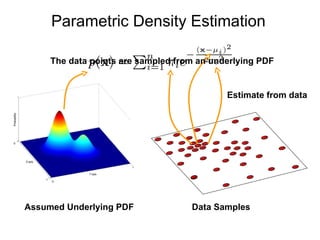
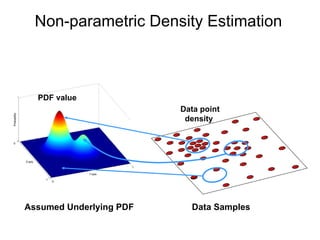
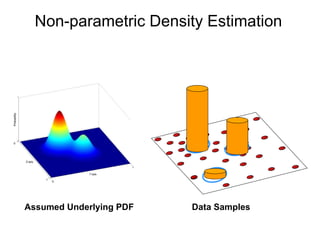
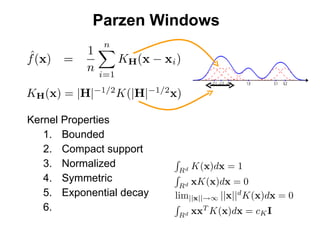
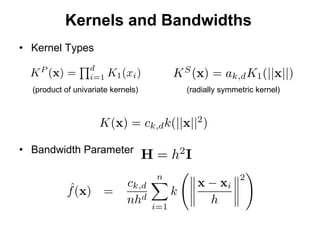
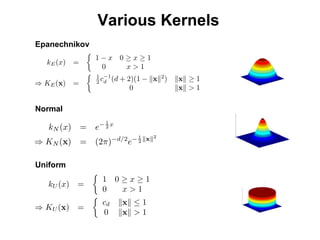
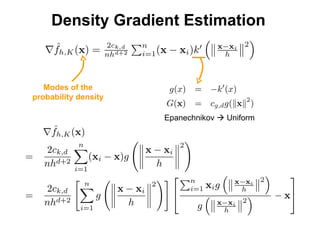
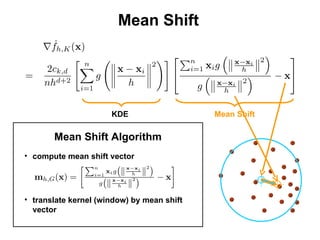
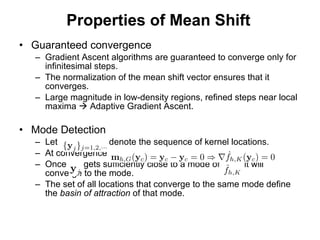
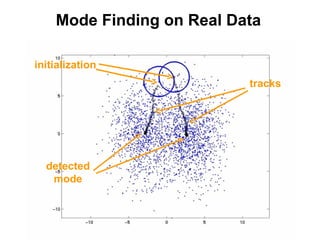
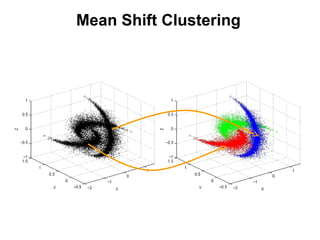
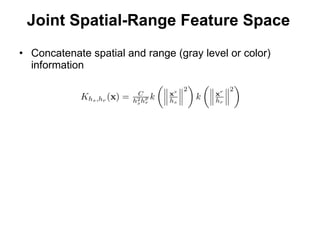
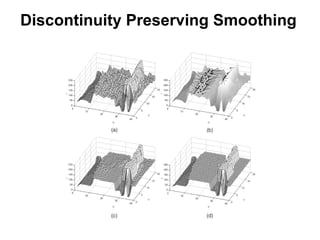
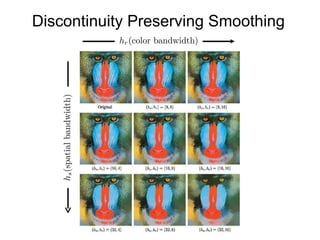
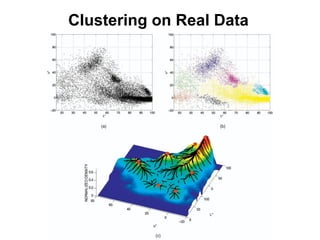
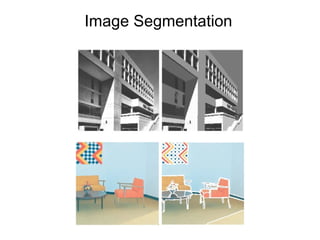
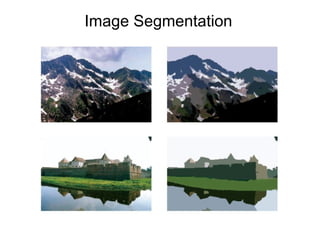
The document discusses the mean shift algorithm, a non-parametric technique for analyzing complex multimodal feature spaces and estimating the stationary points (modes) of the underlying probability density function without explicitly estimating it. It provides an intuitive description of mean shift using a distribution of billiard balls, and outlines how mean shift uses kernel density estimation to perform gradient ascent and converge at the densest regions, allowing it to be used for tasks like mode detection, clustering, and image segmentation.