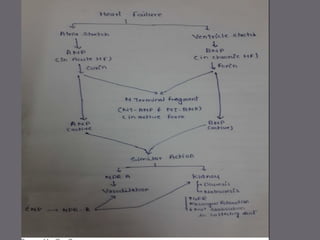
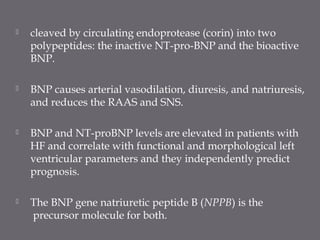
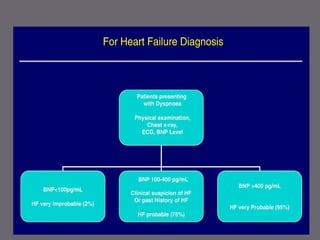
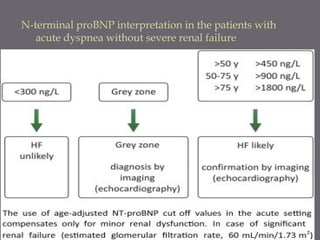
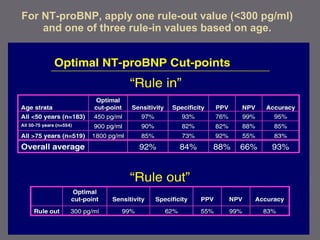
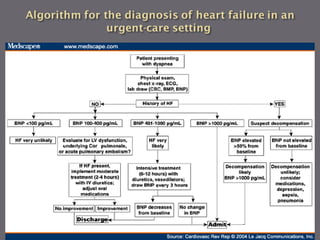
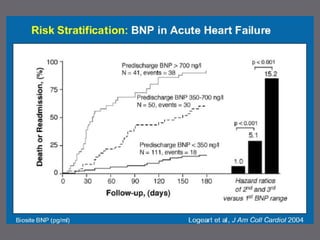
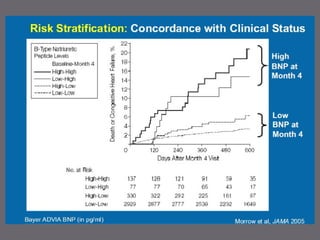
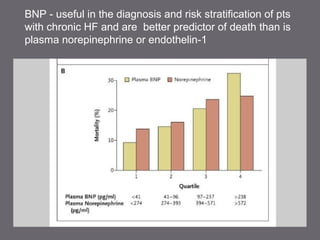
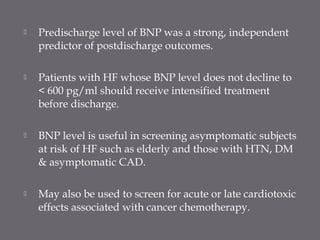
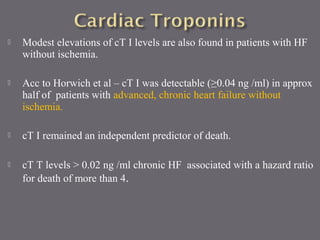
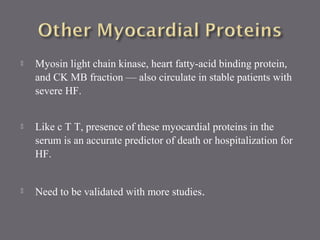
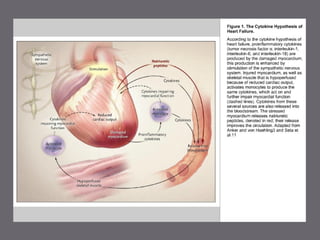
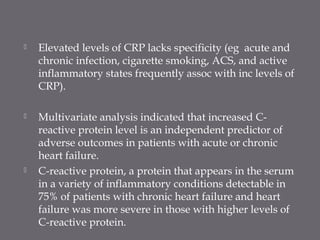
The document discusses various biomarkers used in the diagnosis and management of heart failure. It states that natriuretic peptides like BNP and NT-proBNP are the most widely used biomarkers for heart failure as they are accurate for establishing diagnosis, determining severity, and predicting prognosis. It describes the release and function of these peptides. It also mentions other biomarkers like cardiac troponins, inflammatory markers, neurohormonal factors, and matrix proteins that provide additional information on myocardial injury, inflammation, neurohormonal activation, and remodeling in heart failure. A multimarker approach may help better classify and risk stratify heart failure.