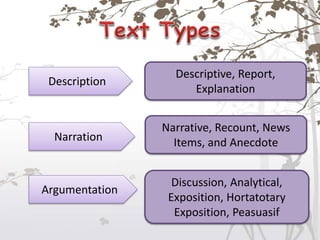
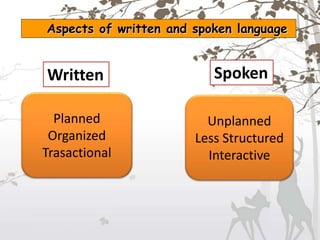
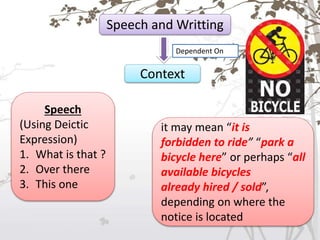
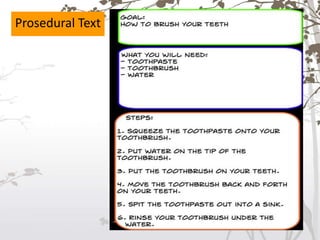
This document discusses the key differences between written and spoken language. It notes that written language is more planned and organized, while spoken language is more unplanned and interactive. Grammatically, written language tends to use complete sentences while speech uses idea units. Vocabulary is also more complex in written works. However, explicitness can depend on context rather than the medium alone. Both written and spoken language serve important communicative functions.