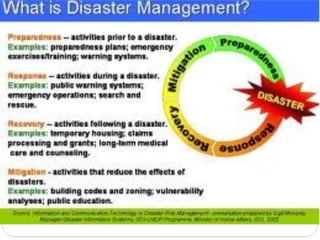
The document discusses disaster nursing, covering the definition of disasters, types of disasters (both natural and man-made), and the principles of disaster management, which includes prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery phases. It outlines the vital role nurses play in disaster scenarios, emphasizing community assessment, disaster planning, and evaluation of disaster response effectiveness. Additionally, it highlights the involvement of international agencies in aiding disaster management efforts.