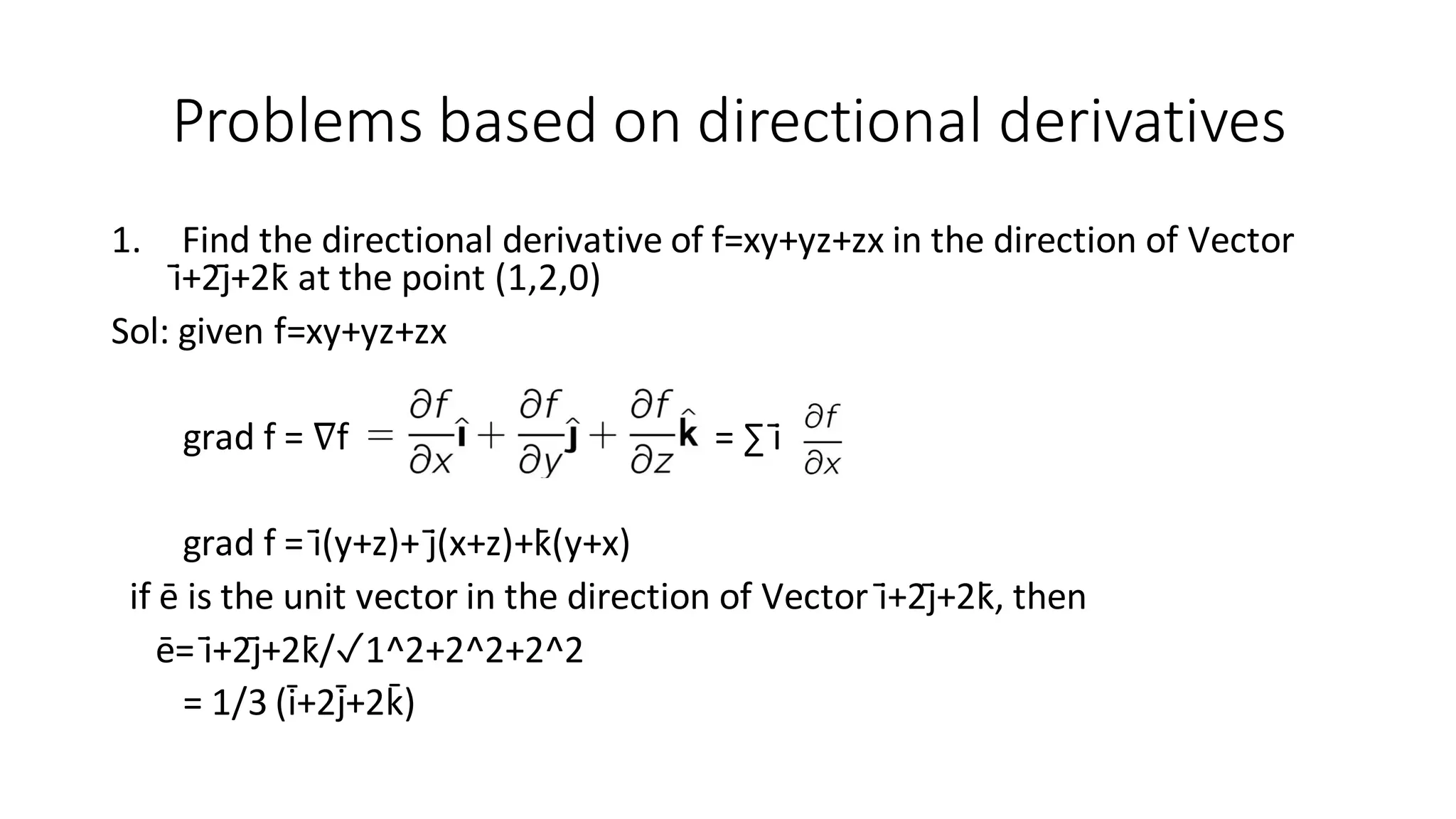
This document discusses directional derivatives and provides examples of calculating them. It defines a directional derivative as the component of the gradient of a function in the direction of a unit vector. The gradient of a function represents the rate of change and is a vector. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the directional derivative of a function at a point in a given direction, as well as finding a unit normal vector to a surface at a point.


![4. If [ā,b̄,c̄]=0 then ā,b̄,c̄ are co-planar.
5. grad ∅=∇∅ is a vector whose three components are , , .
6. ∇∅ may be considered as the result produced when the operator
acts on ∅ (or) ∇∅ may be assumed to be the
multiplication of vector by a scalar ∅.
❑The symbol ‘∇‘ is knownas Vector Differential Operator due
to it’s dual character(∇ is a operator and a vector).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathspresentationg-200618151149/75/Directional-Derivatives-vector-differenciation-3-2048.jpg)
![• Directional derivative of f along the given direction= ē.∇f
= 1/3 (ī+2j̄+2k̄) . (Y+z)ī + (x+z)j̄ + (x+y)k̄ at (1,2,0)
= 1/3 [ (Y+z) + 2(x+z) + 2(x+y)] at (1,2,0)
= 1/3 [(2+0) + 2(1+0) + 2(1+2)
= 1/3 (2+2+6)
= 1/3 (10)
= 10/3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathspresentationg-200618151149/75/Directional-Derivatives-vector-differenciation-5-2048.jpg)

