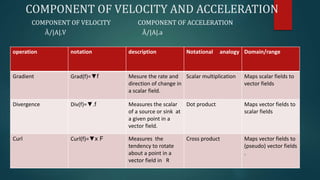
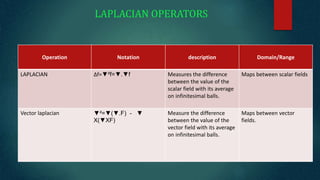
This document provides an introduction to vector calculus concepts. It defines key terms like velocity, acceleration, and gradient. It presents the formulas for calculating the gradient of a scalar function, unit normal vector, and components of velocity and acceleration. Additionally, it outlines vector operations like divergence, curl, and Laplacian operators; and provides examples of how to calculate a scalar potential, directional derivative, and conditions for solenoidal and irrotational vectors.