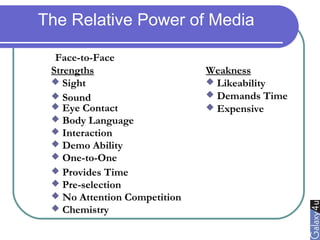
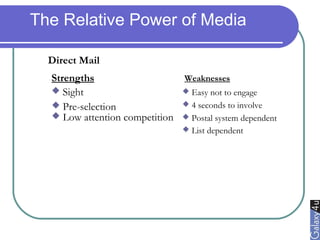
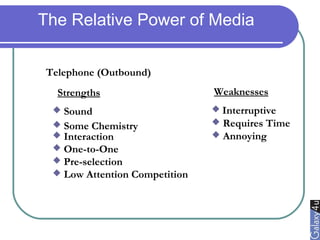
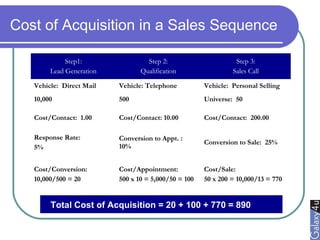
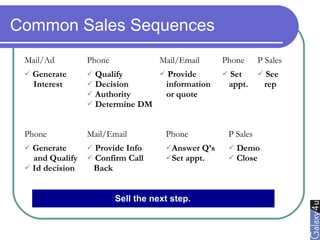
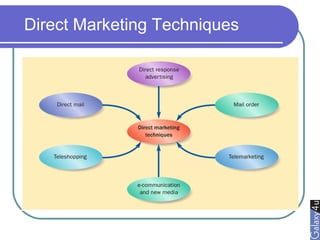
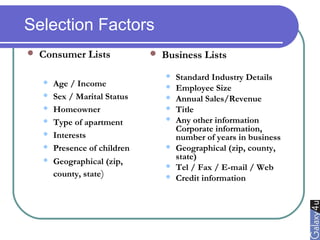
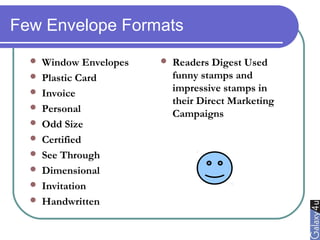
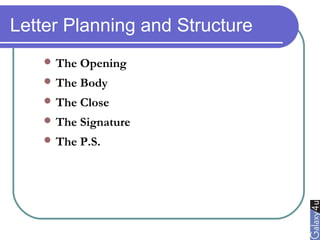
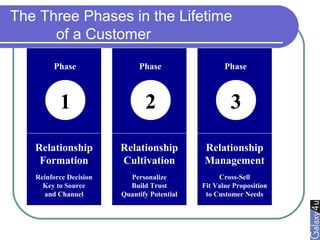
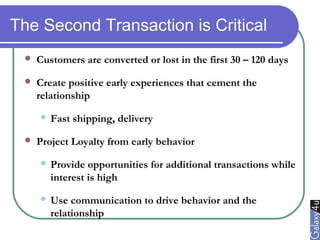
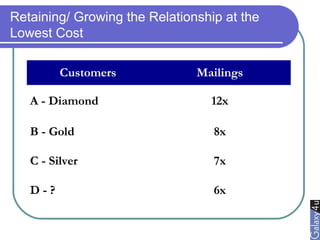
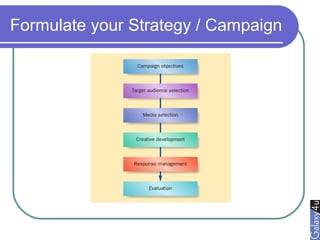
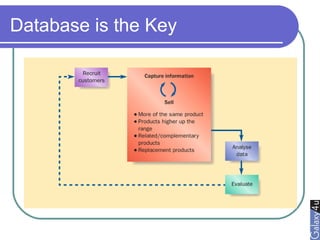
Direct marketing is a method that fosters individual relationships with prospects, contrasting with general advertising's broad approach. It involves targeted communications to provoke immediate responses and build long-term relationships, supported by a defined sales sequence and various techniques for customer engagement. Effective direct marketing requires careful selection of audience, relevant offers, and strategic follow-ups to maximize customer acquisition and retention.