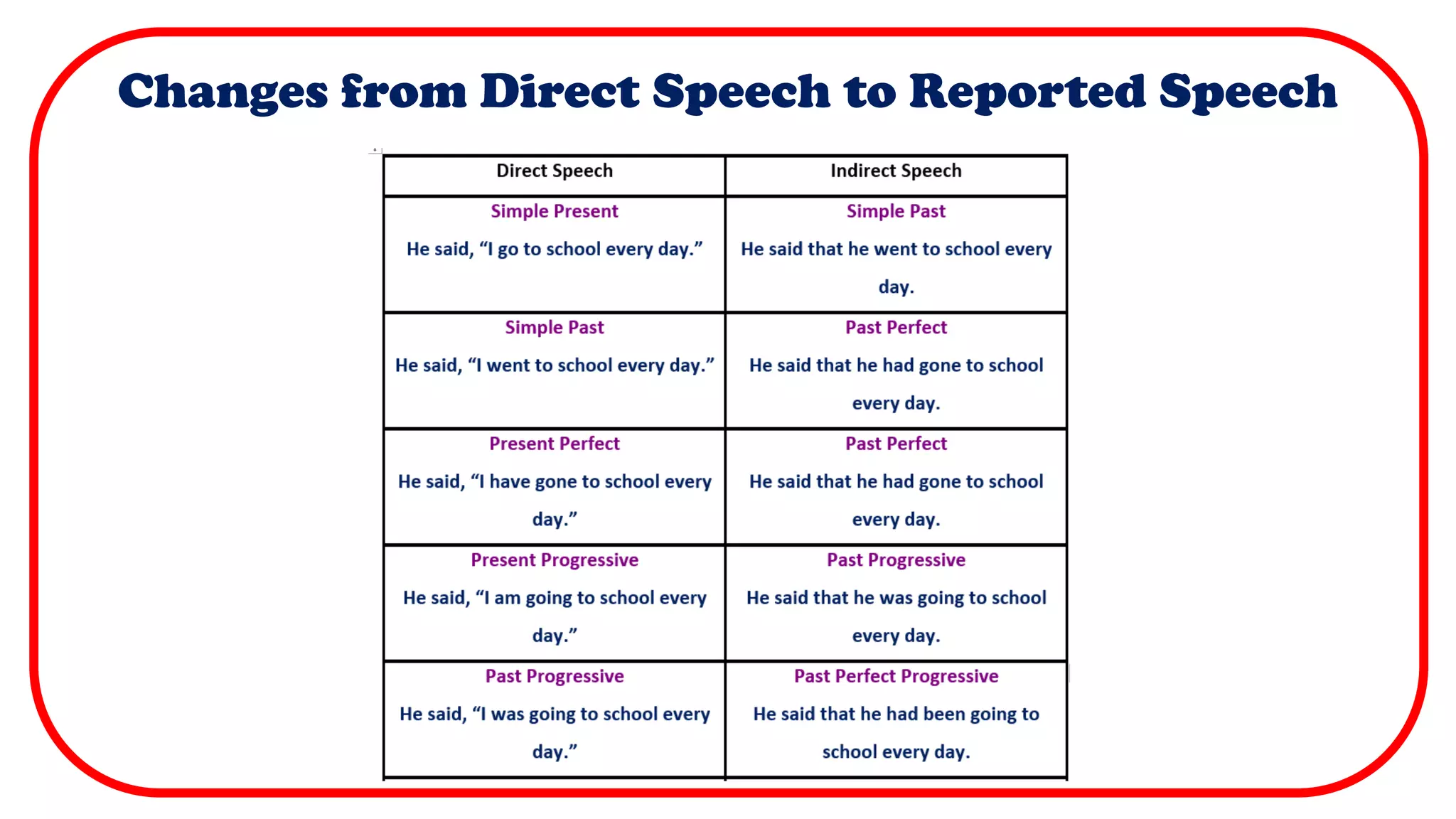
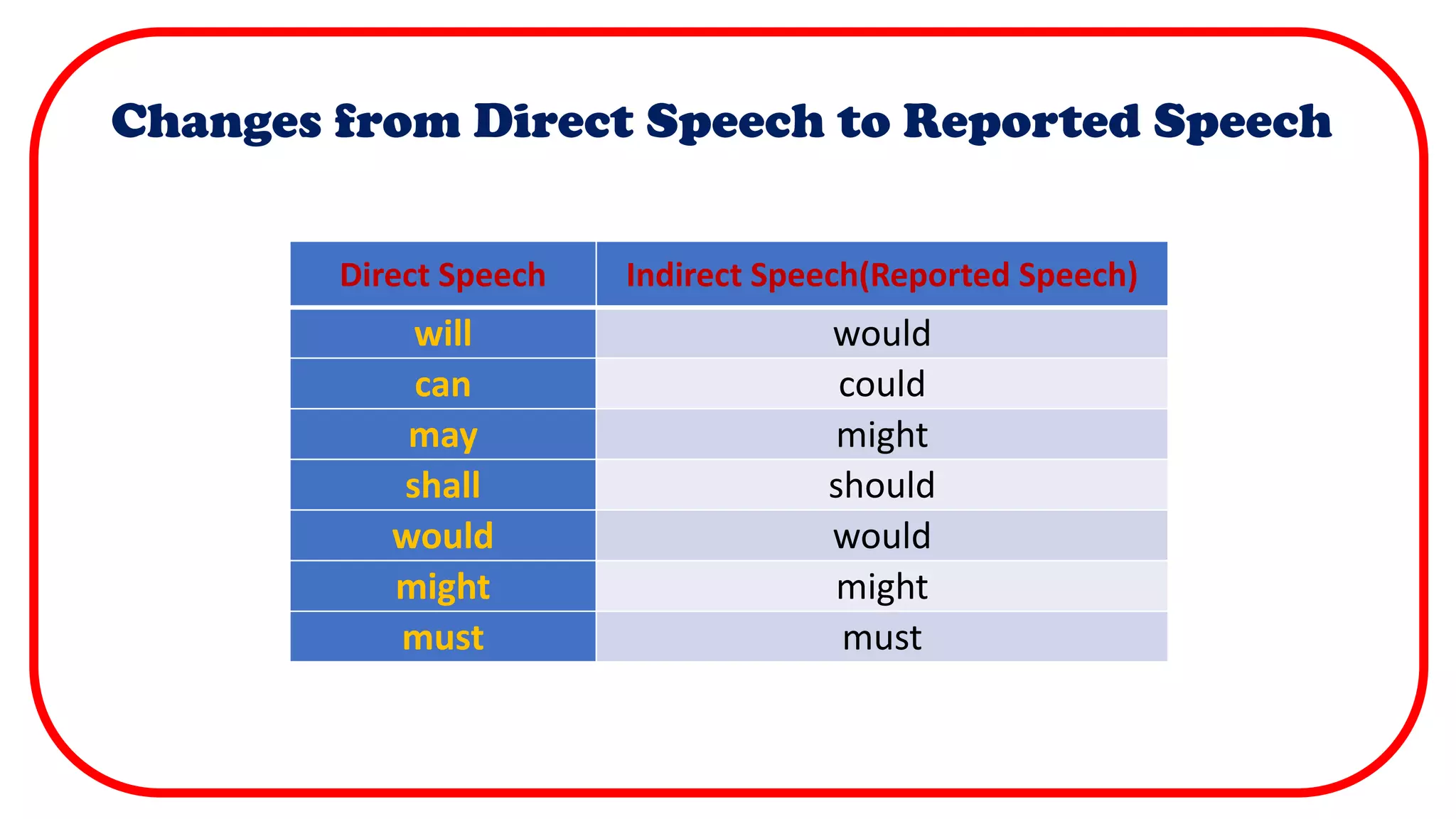
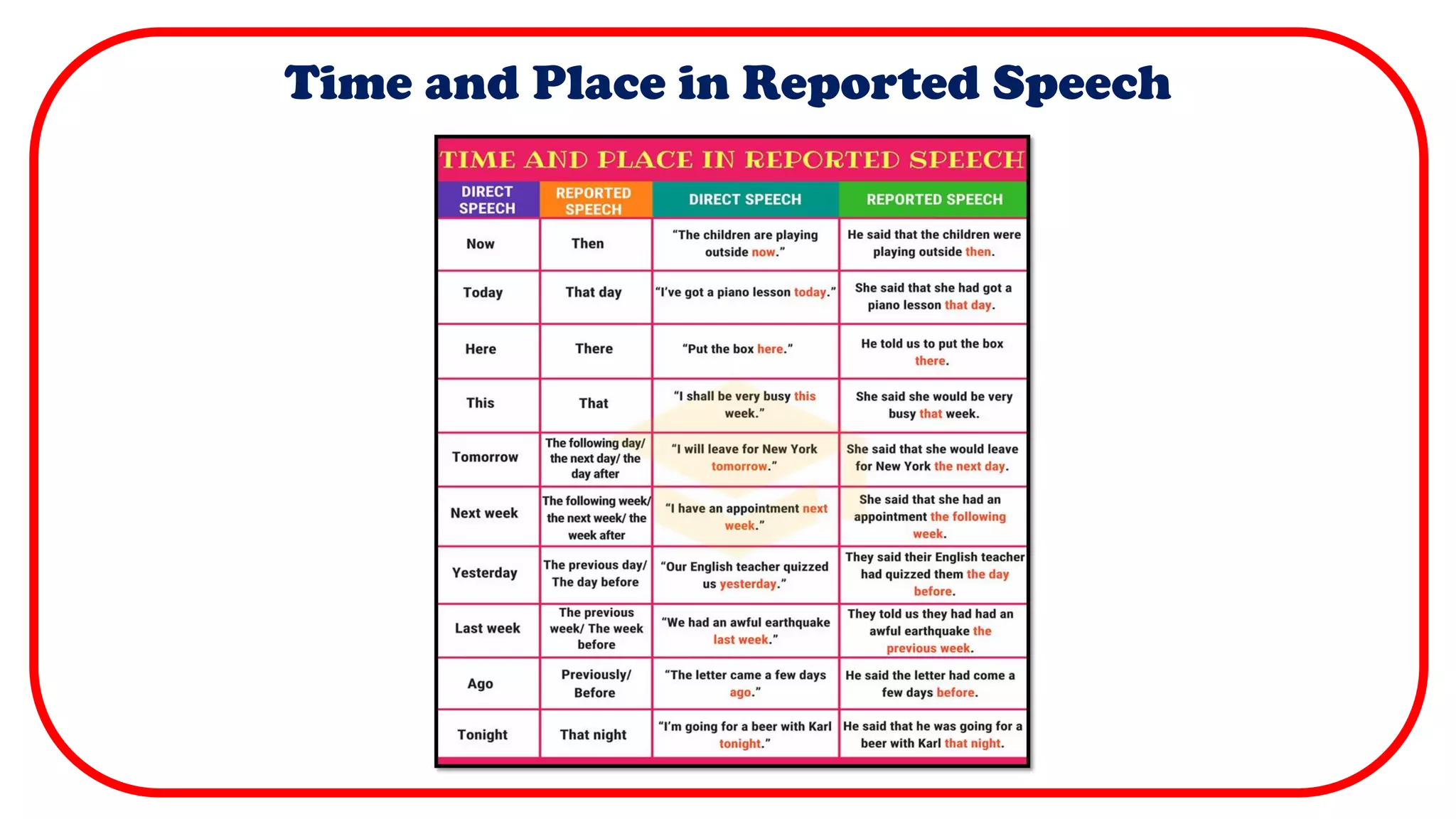
Direct speech uses quotation marks to indicate the exact words spoken by a person. It requires a new line for each new speaker and capitalizes the first word of each quotation. Indirect or reported speech does not use quotation marks and changes verbs and pronouns to reflect when the words were spoken rather than the exact words. It summarizes the key details on using quotation marks, capitalization, punctuation and verb tense changes between direct and reported speech.