Embed presentation
Download to read offline




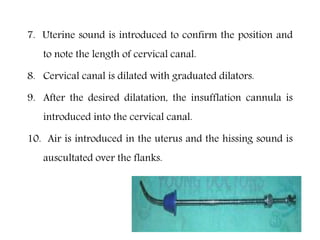

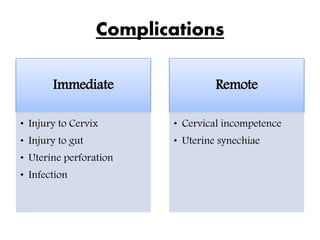
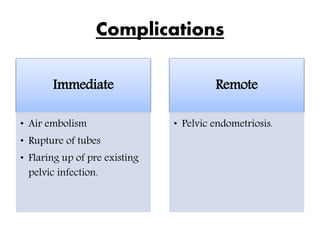


Dilatation and insufflation (D&I), also known as Rubin's test, is performed to assess the patency of fallopian tubes, typically for fertility investigations or following tuboplasty. The procedure involves several steps including cervical dilation, air insufflation into the uterus, and monitoring for audible sounds to confirm results. Complications can arise immediately or remotely, including injury to the cervix or gut, infection, and the potential for pelvic endometriosis.








