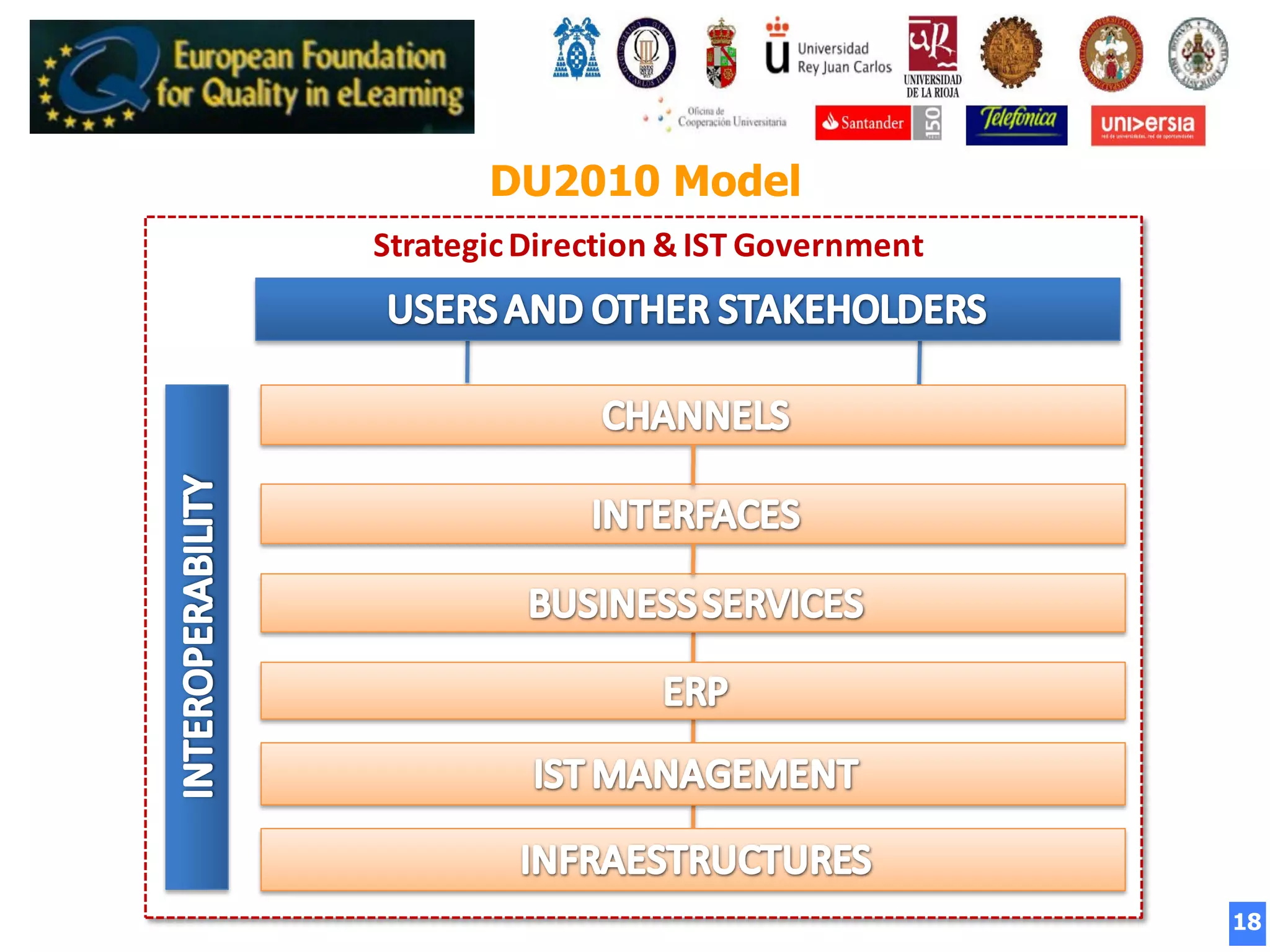
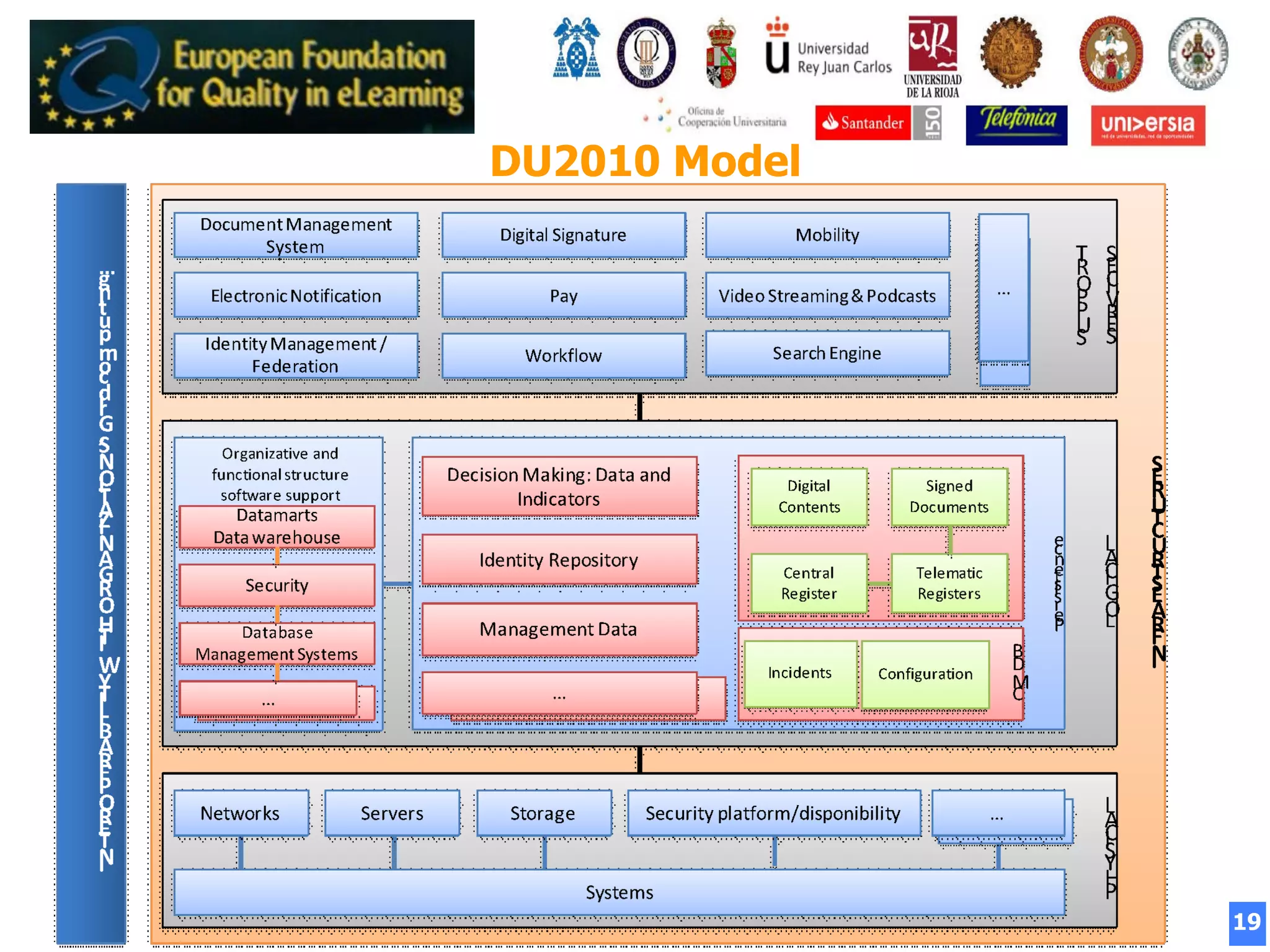
The document summarizes the Digital University 2010 White Paper presented at the University of Salamanca in 2008. It proposes a new model for universities in the digital age, focusing on internationalization, flexibility, distance learning, excellence, quality, and transparency. The model emphasizes technology, services, management, and interoperability across functional areas and interfaces. It aims to adapt Spanish and European universities for the digital world and knowledge society.