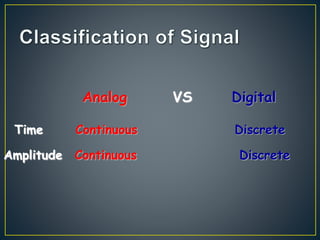
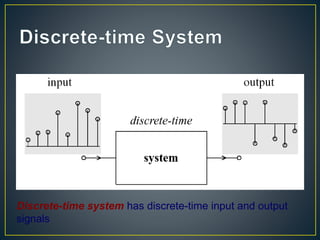
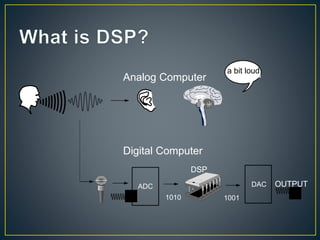
The document discusses digital signal processing (DSP). It begins by defining analog and digital signals, noting that analog signals are continuous while digital signals are discrete. It then outlines the basic components of a DSP system, including an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to digitize the input signal, a digital signal processor to perform operations on the digital signal, and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to reconstruct the analog output signal. Finally, it lists some advantages and limitations of DSP systems compared to analog systems, and provides examples of DSP applications.