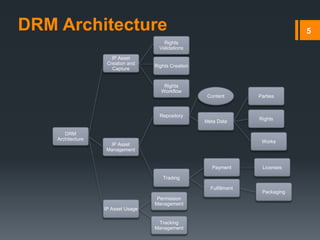
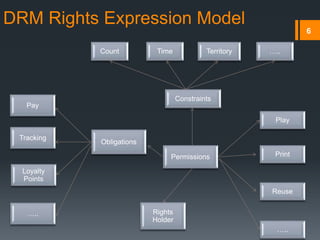
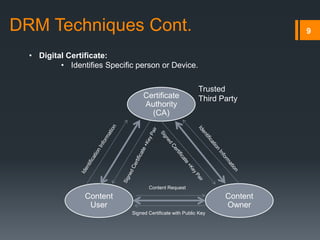
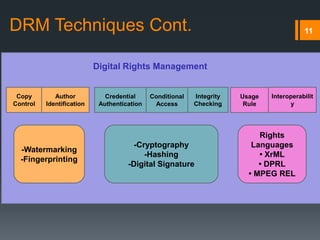
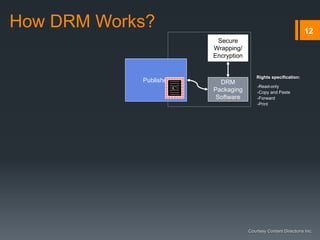
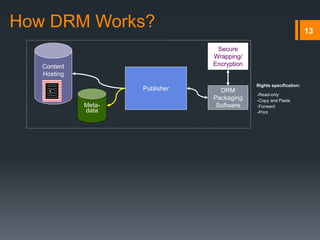
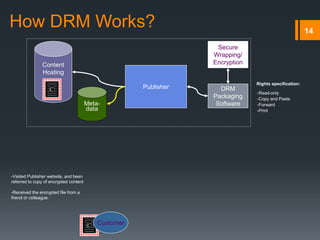
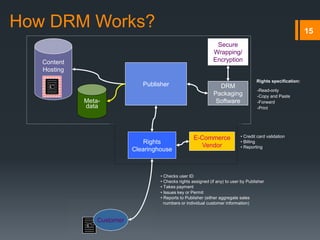
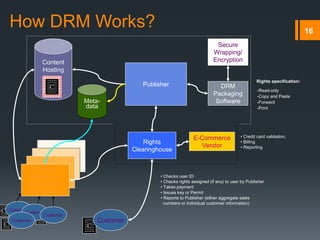
Digital rights management (DRM) refers to technologies that protect digital content by restricting access and use. DRM allows content owners to control how consumers access and use content, as well as track operations on the content. Common DRM techniques include encryption, digital certificates, watermarking, and rights specification languages. DRM provides advantages for content owners such as protecting intellectual property rights and allowing for more efficient monitoring of sales, but can also restrict what consumers can do with content they have purchased.