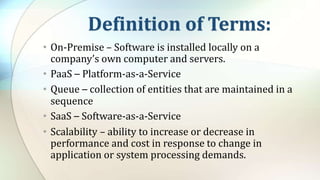
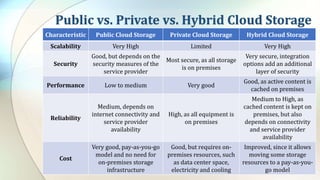
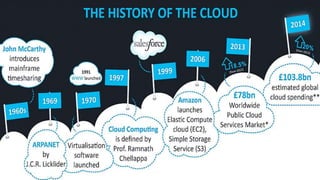
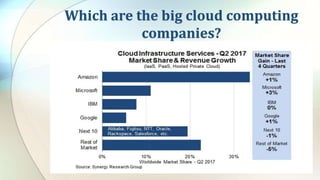
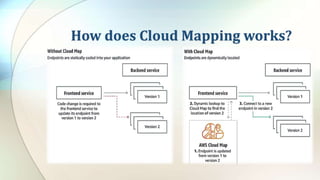
This document defines key cloud computing and cloud storage terms and concepts. It distinguishes between cloud storage, which saves and shares data, and cloud computing, which allows remote work on data. Key differences are that cloud computing requires more processing power while cloud storage needs more storage space. The document also outlines public, private, and hybrid cloud models and major cloud vendors. It introduces cloud mapping as a service that maintains updated resource locations.