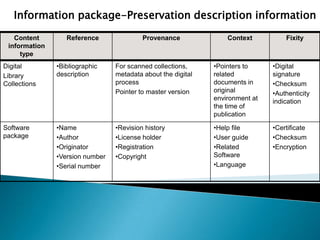
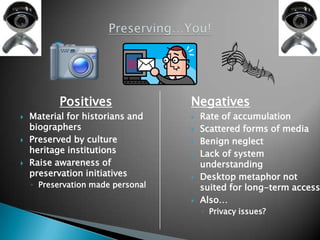
This document discusses the key aspects and challenges of digital preservation including:
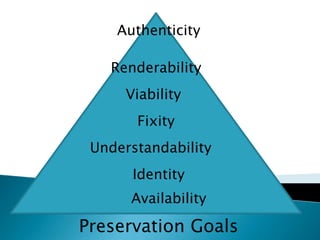
- Ensuring the authenticity, renderability, viability, fixity, understandability, and identity of digital materials over time.
- Threats such as media and format obsolescence and the need for periodic copying and migration to new formats.
- International efforts to develop standards, strategies, and software for digital preservation.
- Obstacles including issues around preserving links, original look and feel, and personal digital materials scattered across media.