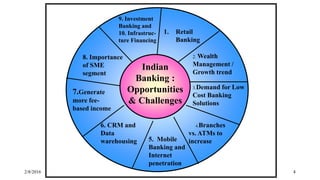
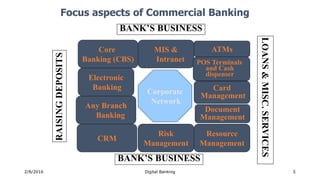
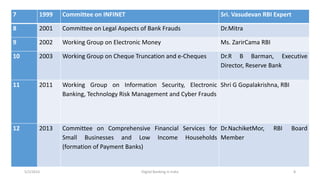
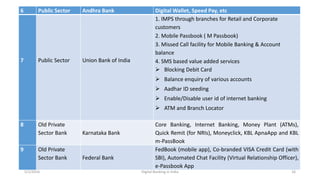
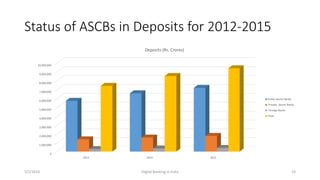
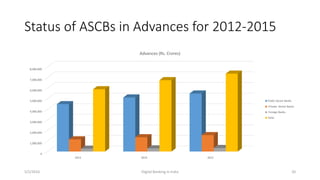
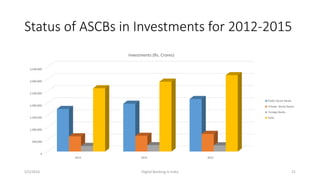
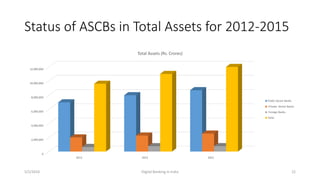
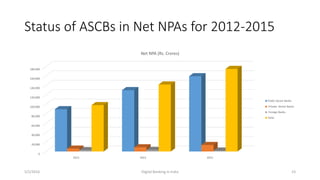
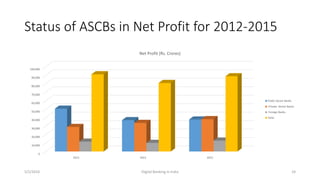
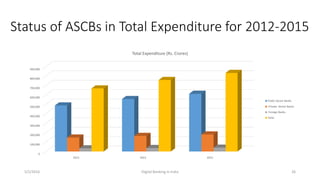
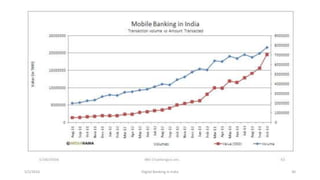
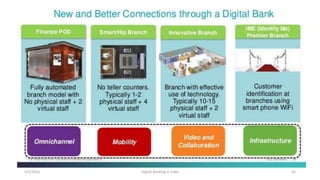
The document summarizes a presentation given on digital banking in India. It provides an overview of the Indian banking system and reforms, discusses various committees formed by the RBI to advance banking technology. It also reviews literature on digital banking, outlines the objectives and methodology of the study. Additionally, it examines guidelines from RBI on payments and settlements, the role of IDRBT in digital banking frameworks. Finally, it analyzes the various digital banking products and services offered by major public sector banks in India like SBI, PNB and others.