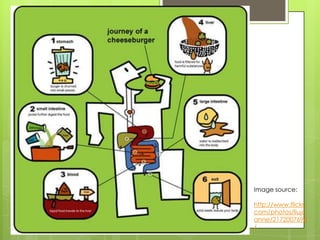
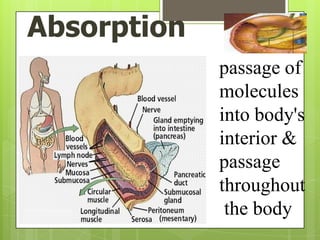
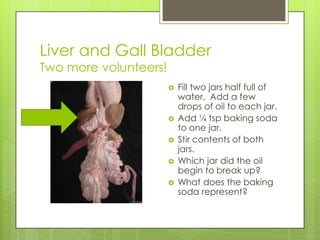
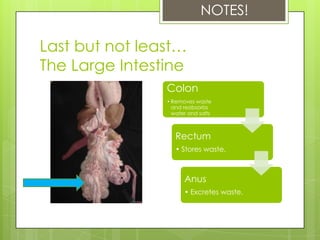
The document summarizes key aspects of the digestive system. It discusses three main functions:
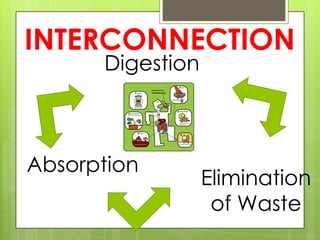
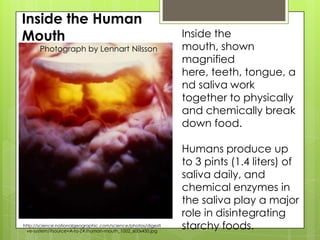
1. Digestion - The breakdown of food into smaller molecules through mechanical and chemical processes in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Enzymes in saliva and gastric juice aid in digestion.
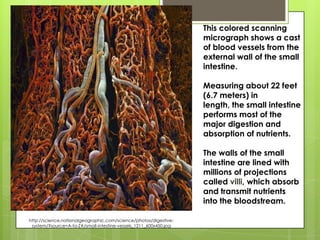
2. Absorption - Nutrients are absorbed through the walls of the small intestine, especially in structures called villi, and passed into the bloodstream.
3. Elimination - Undigested wastes are passed through the large intestine, rectum and anus and excreted from the body.