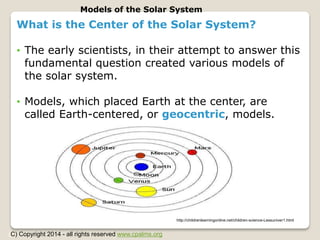
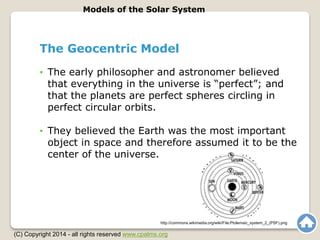
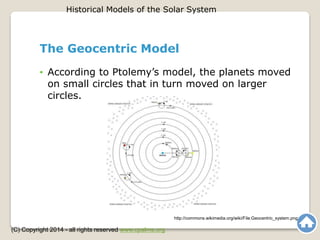
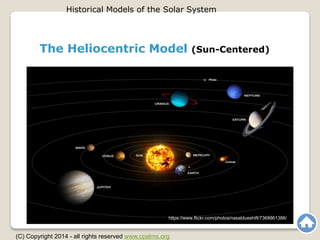
The document outlines the historical models of the solar system, focusing on the geocentric model, which placed Earth at the center, and the heliocentric model, which centers on the Sun. Early astronomers like Aristotle and Ptolemy advocated geocentrism, while Copernicus and later Galileo proposed and supported the heliocentric model, which became widely accepted due to its alignment with observational evidence. The text emphasizes the evolution of astronomical thought over time and highlights key figures and their contributions to the understanding of celestial systems.