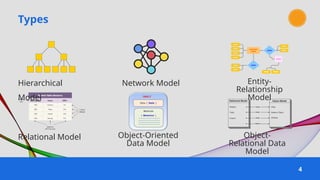
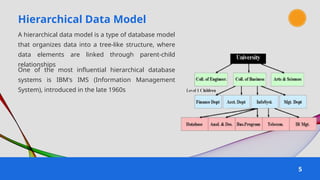
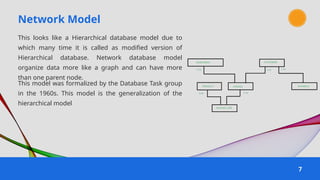
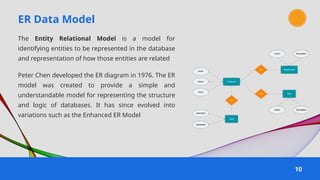
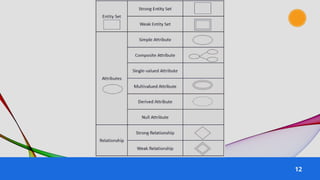
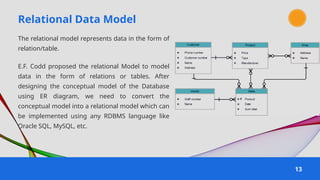
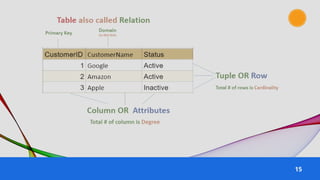
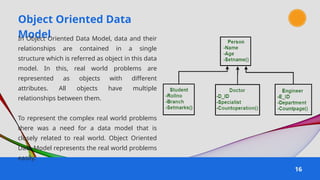
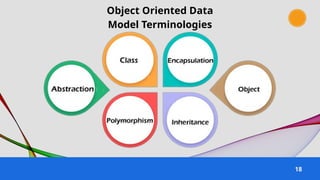
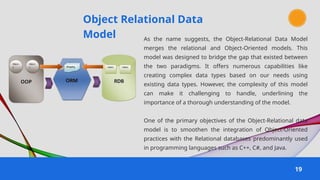
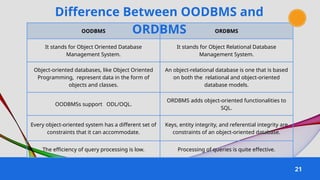
The document provides an overview of various data models used in database management systems, including relational, hierarchical, network, entity-relationship, object-oriented, and object-relational models. It discusses the definitions, advantages, and disadvantages of each model, along with their structural characteristics and usage scenarios. The importance of understanding these models for effective data organization and management in databases is emphasized.