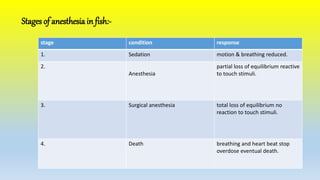
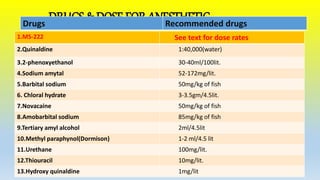
This document discusses the use of anesthetics in fish breeding and transport. It notes that fish can be stressed by handling and transport, so anesthetics are used to prevent injury and reduce metabolism. Commonly used anesthetics include MS-222, quinidine, 2-phenoxyethanol, and clove oil. Anesthetics induce sedation, partial loss of movement, or full anesthesia in fish. They are beneficial as they reduce stress on fish and allow for safer breeding, transport, and sampling. The document provides dosages for various anesthetics and details their effects on fish.