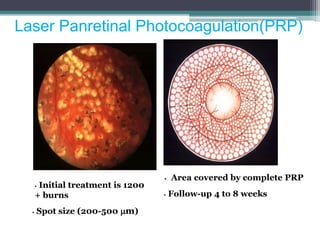
Diabetic retinopathy is progressive dysfunction of retinal blood vessels due to hyperglycemia. It is the leading cause of blindness among working-age adults. The risk increases with duration of diabetes and is also increased by hypertension, smoking, and renal disease. Early stages are asymptomatic but can progress to proliferative diabetic retinopathy with neovascularization, potentially leading to vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. Treatment depends on severity and may include laser photocoagulation, intravitreal injections, or vitrectomy surgery. Regular screening is important to detect diabetic retinopathy early and prevent vision loss.