This document discusses diabetic retinopathy, including:
- Criteria for diagnosing diabetes and risk factors for type 2 diabetes such as family history, obesity, and hypertension.
- Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in working-age adults and risk increases with duration of diabetes and poor blood sugar control.
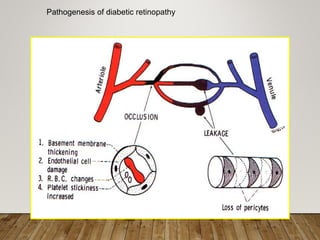
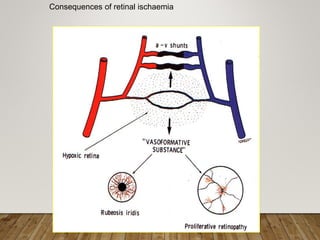
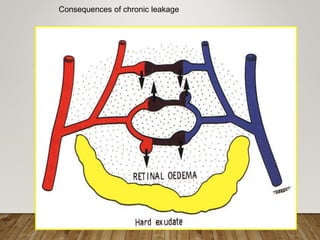
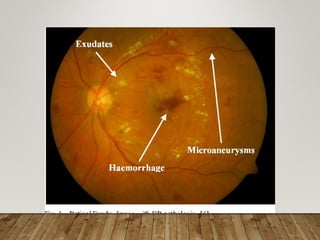
- Pathogenesis involves microvascular occlusion leading to ischemia, hypoxia, and new abnormal blood vessel growth which can cause vision loss if left untreated.
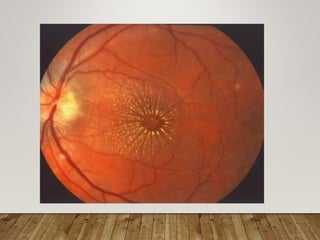
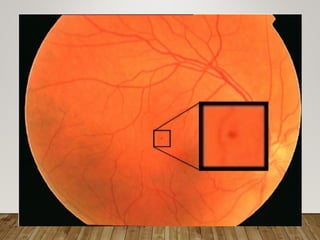
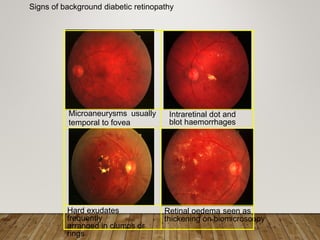
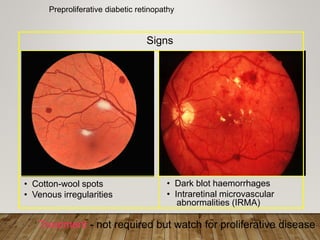
- Stages include background, pre-proliferative, and proliferative retinopathy each with characteristic signs.
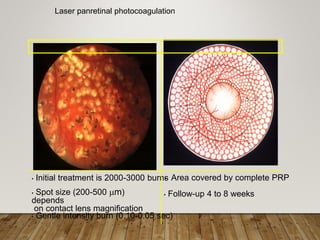
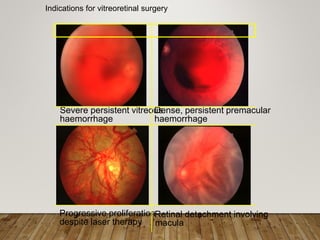
- Treatment depends on stage but may include anti-VEGF drugs or laser photocoagulation surgery to prevent