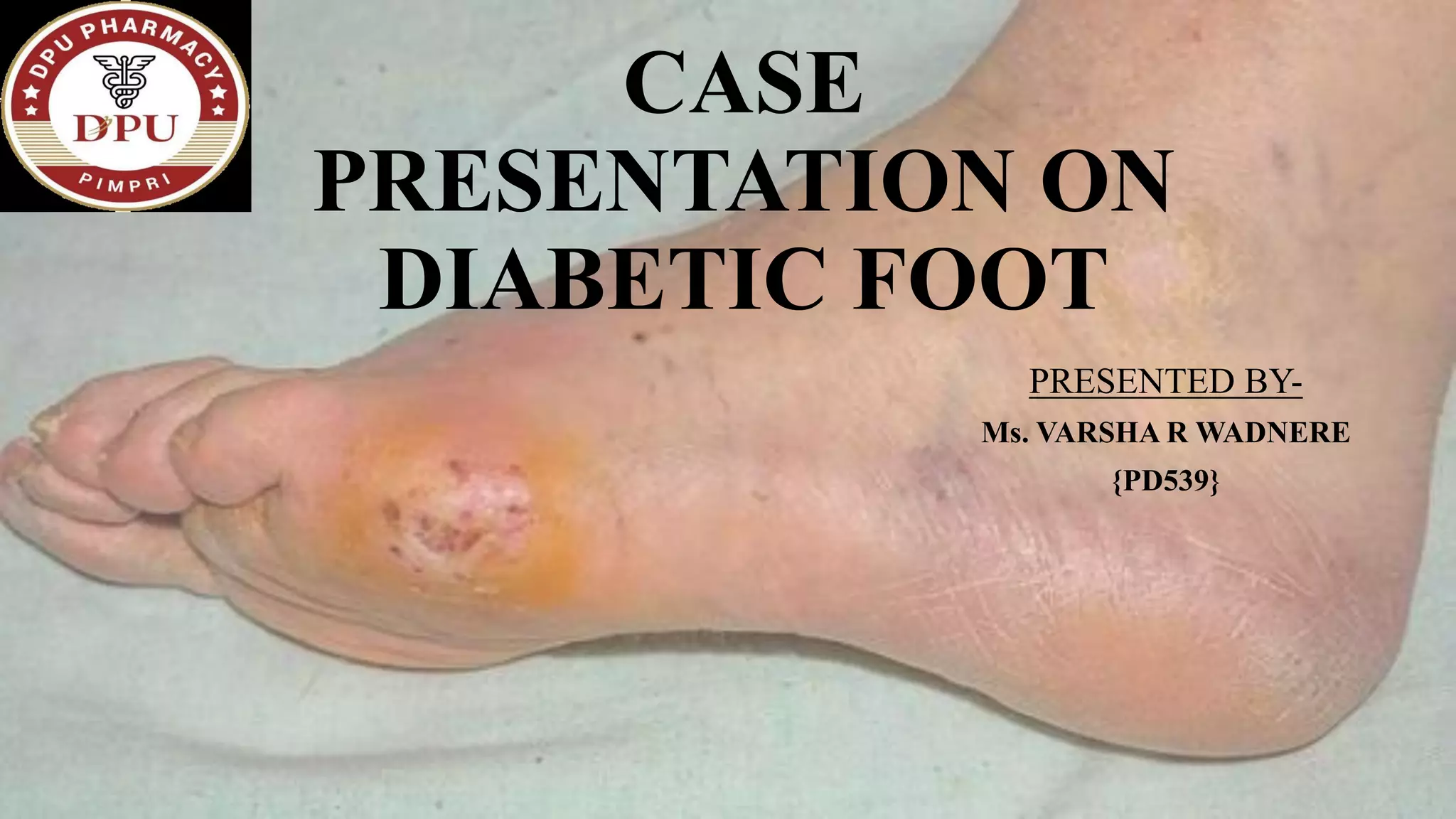
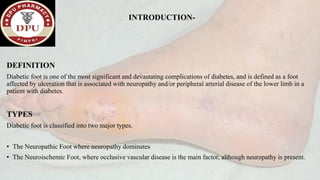
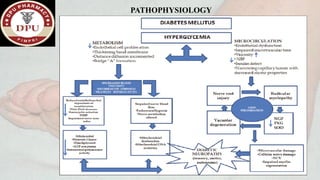
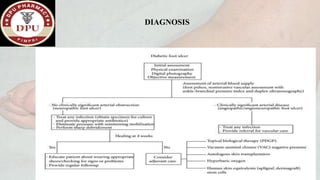
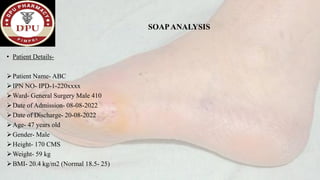
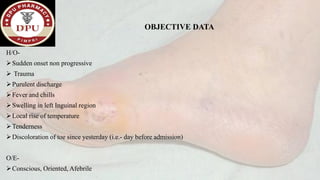
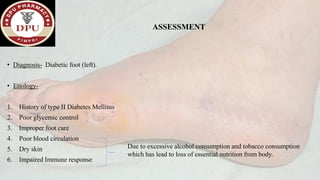
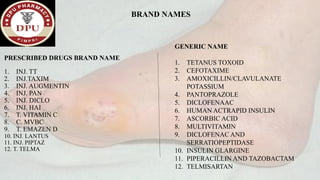
1. The document presents a case of diabetic foot in a 47-year old male with type 2 diabetes and a history of alcohol and tobacco use. He presented with pain and discharge in his left great toe.
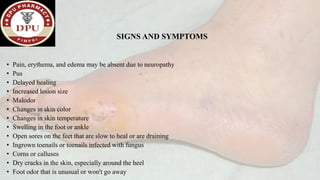
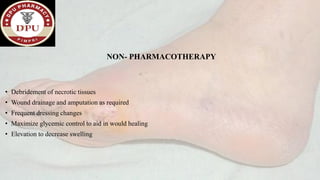
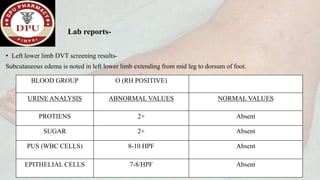
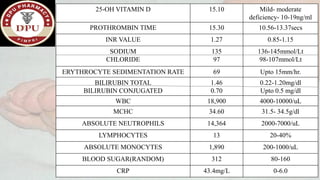
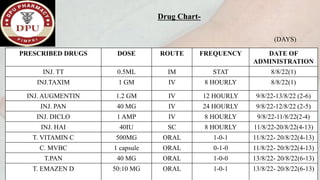
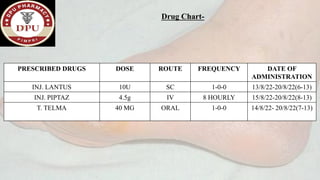
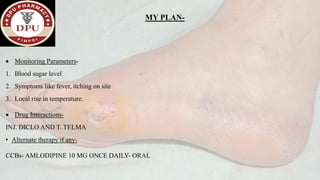
2. On examination, he had signs of infection in the left foot. He was treated with antibiotics, wound debridement, and amputation of the left great toe.
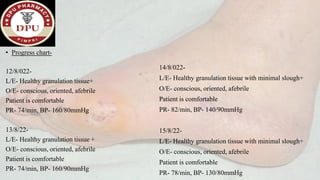
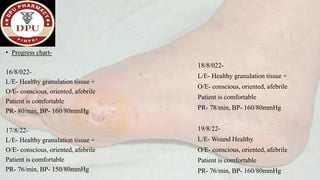
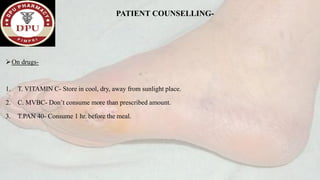
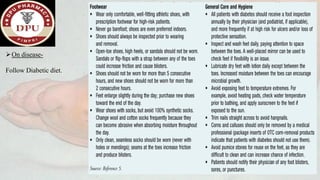
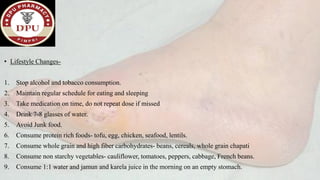
3. After treatment, his symptoms improved and he was discharged with medications and lifestyle recommendations to prevent recurrence of diabetic foot complications.