This document provides an overview and analysis of several sociological theories of deviance:
1) Functionalism views deviance as serving important social functions like affirming norms and pushing boundaries for social change.
2) Conflict theory sees deviance as reflecting power imbalances in society with those lacking resources turning to crime.
3) Labeling theory argues that deviance occurs when a negative label is applied and then adopted.
4) Differential association theory claims criminal behavior is learned through interactions where criminal values and techniques are communicated.
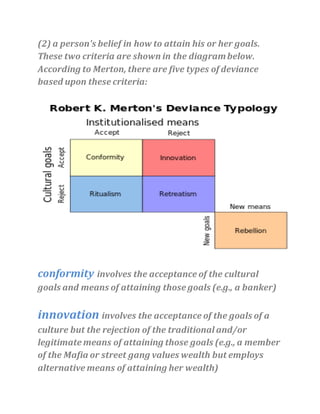
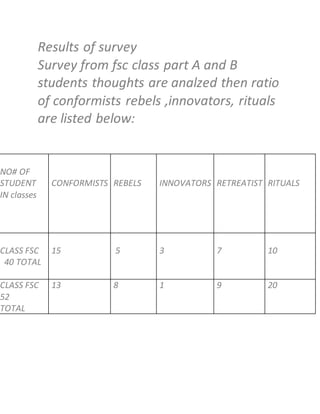
5) A survey of students found varying rates of conformity, rebellion, innovation and retreatism among the respondents.

![Content
1] Introduction
2] Concepts
3] Functionalist view
4] Conflict theory
5] Strain theory
6] Labeling theory
7] Deviance and crime
8] Results of survey
9] Class activity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deviance2-170416103612/85/Deviance-2-2-320.jpg)






![CLASS ACTIVITY:
Ask questions:
1] which theory explains deviance in better way
2] why crime create social disorder?
3] how to reduced crimes like murder ,child and
woman absue , etc is that due to mental or physical
illness?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deviance2-170416103612/85/Deviance-2-12-320.jpg)