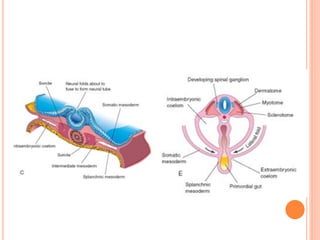
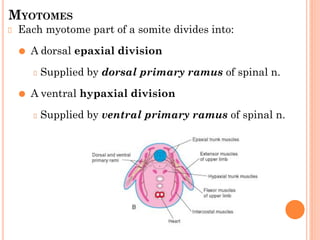
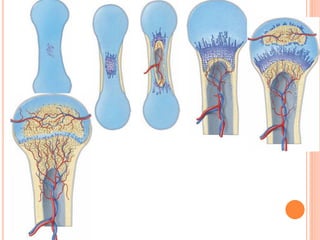
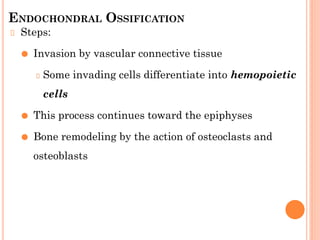
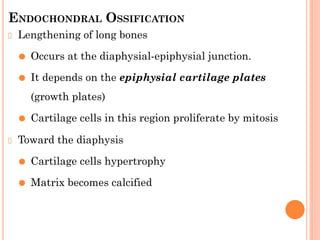
Skeletal muscle, bone, and cartilage develop from mesenchymal precursor cells. Skeletal muscle develops from myoblasts that fuse to form myotubes. Bone develops through either intramembranous or endochondral ossification, where mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts or chondroblasts to lay down bone or cartilage matrices. Long bones develop primarily through endochondral ossification, where cartilage models are replaced by bone through invasion of blood vessels and differentiation of cells. Growth and remodeling of bones continues postnatally through the coordinated action of osteoclasts and osteoblasts.