This document provides an overview of the development of international relations in 6 stages:
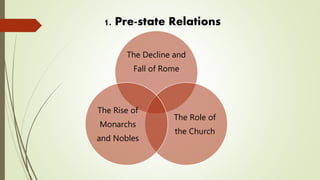
1) Pre-state relations including the decline of Rome, the role of the church, and rise of monarchs and nobles
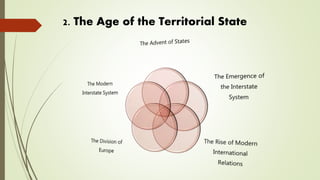
2) The age of the territorial state
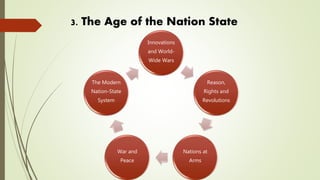
3) The age of the nation state including innovations, wars, revolutions, and the modern nation state system
4) Non-Western politics including colonialism and imperialism
5) The 20th century including industrialism, World War I, and the division of the world after World War II
6) The post-Cold War world
It then provides more details on some of the subtopics within these stages, such as the political and economic impacts of