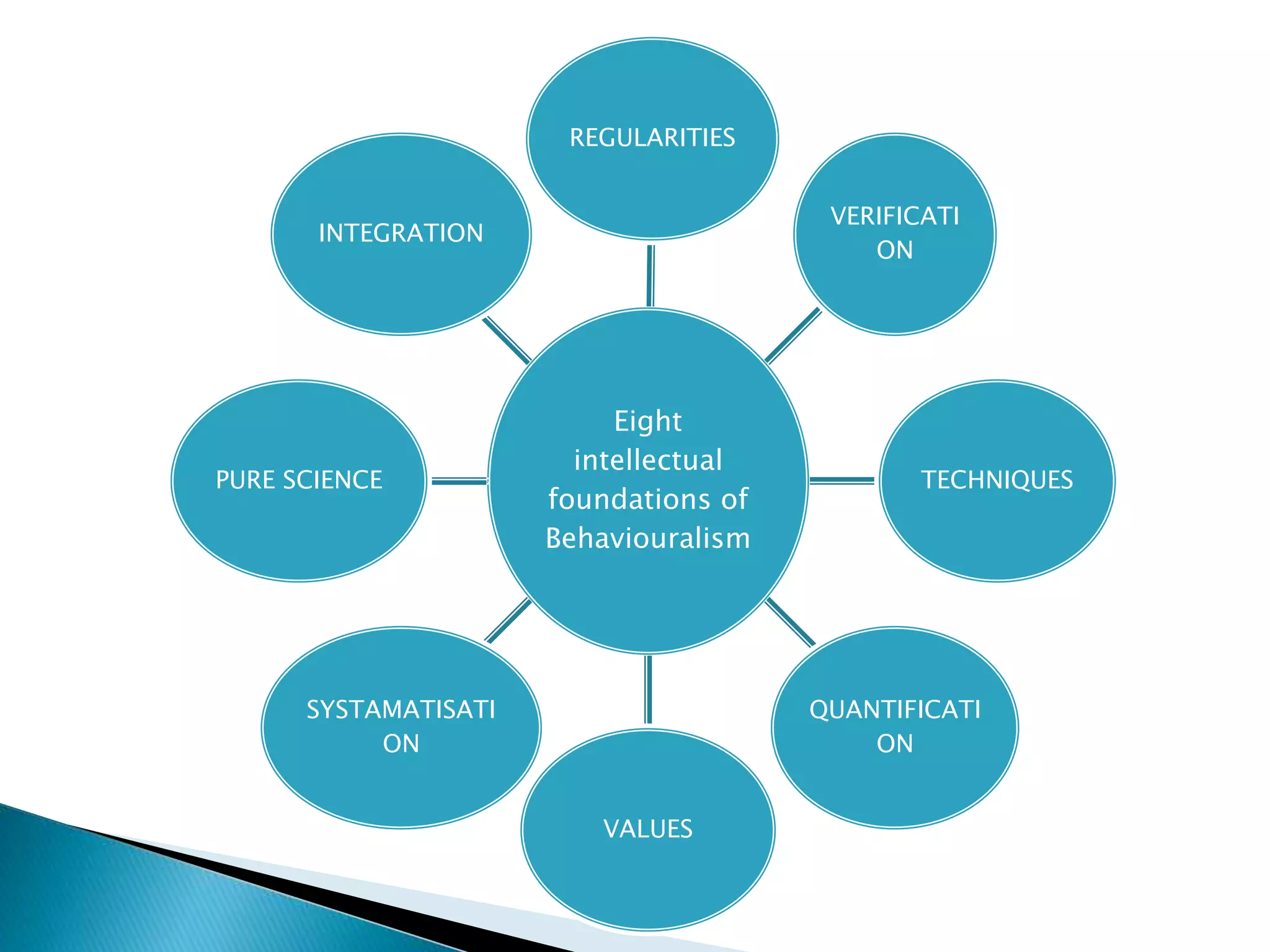
This document discusses the behavioral approach in political science. It began as a post-World War II protest movement against traditional approaches. Key exponents like Charles Merriam advocated studying political phenomena through observation and measurable data to make the field more scientific and value-free. The behavioral approach focuses on the political behaviors of individuals and groups within political systems. It aims to understand political events by analyzing observable human behavior rather than values or outcomes. However, critics argue that political science cannot be entirely value-free and human behavior is not static.