Development of dentition and occlusion
- 1. Development of Dentition and Occlusion PROF (Dr.) SAIBEL FARISHTA
- 2. Development Of Teeth The embryonic oral cavity is lined by stratified squamous epithelium known as oral ectoderm. Around the 6th week of intra-uterine life the infero-lateral border of the maxillary arch and supero-lateral border of the mandibular arch show localized proliferation of the oral ectoderm resulting in the formation of horse-shoe shaped band of tissue called the dental lamina. The dental lamina plays an important role in the development of the dentition. The dec. teeth are formed by direct proliferation of dental lamina. All teeth originate from the dental lamina.
- 3. The ectoderm in certain areas of the dental lamina proliferates and forms knob-like structures that grow into the underlying mesenchyme. Each of these knobs represent a future dec. tooth and is called the enamel organ. The enamel organ passes through a number of stages ultimately forming the teeth. Based on the shape of enamel organ, the development of teeth can be divided into 3 stages – bud, cap and bell stage.
- 4. Bud Stage - This is the initial stage of tooth formation where the enamel organ resembles a small bud. In this stage, the enamel organ consists of peripherally located low columnar cells and centrally located polygonal cells. The surrounding mesenchymal cells proliferate resulting in their condensation in two areas. The area of condensation below the enamel organ is the dental papilla. The ectomesenchymal condensation that surrounds the tooth bud and dental papilla is the dental sac. The dental papilla and dental sac is not well defined during this stage. The cells of the dental papilla form the dentine and pulp while the dental sac forms cementum and periodontal ligament.
- 5. Cap Stage - The tooth bud continues to proliferate resulting in a cap shaped enamel organ. This is characterized by a shallow invagination on the under surface of the bud. The outer cells of the cap covering the convexity are cuboidal and are called the outer enamel epithelium. The cells lining the concavity of the cap become tall columnar and are called as the inner enamel epithelium. The central area of the enamel organ between the outer and inner enamel epithelium, which initially consisted of polygonal cells, acquire more intercellular fluid and form a cellular network called the stellate reticulum. The staellate reticulum has a branched network of cells.
- 6. Bell Stage - Due to continued uneven growth of the enamel organ, it acquires a bell shape. The cells of the inner enamel epithelium differentiate prior to amelogenesis into tall columnar cells called ameloblasts which lay down enamel. The cells of the inner enamel epithelium eert a strong influence on the underlying mesenchymal cells of the dental papilla. A few layers of flat squamous cells are seen between the inner enamel epithelium and stellate reticulum. This layer is called the stratum intermedium. The stellate reticulum expands due to continued accumulation of intra- cellular fluid. The cells of this area are star shaped, having large processes that anastamose with adjacent cells. As the enamel formation starts, stratum reticulum collapses to a narrow zone, thereby reducing the distance between the outer enamel and inner enamel epithelium. The cells of outer enamel epithelium flatten to form low cuboidal cells. The outer enamel epithelium is thrown into folds which are rich in capillary network. This provides a source of nutrition for the enamel organ.
- 7. Before the inner enamel epithelium begins to produce enamel, the peripheral cells of the dental papilla differentiate into odontoblasts. These are cuboidal cells that later assume a columnar form and produce dentin. The dental sac exhibits a circular arrangement of its fibers and resembles a capsule around the enamel organ. The fibers of the dental sac form the periodontal fibers that span between the root and bone. The junction between the inner enamel epithelium and odontoblasts outlines the future dentino-enamel junction.
- 8. Root Formation - Root development begins after the dentin and enamel formation reaches the future cemento-enamel junction. The outer and inner enamel epithelium join and form a sheath that helps in molding the shape of the root. This sheath is called the Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath.
- 9. Periods Of Occlusal Development 1. Pre-dental period 2. Deciduous dentition period 3. Mixed dentition period 4. Permanent dentition period 1. Pre-Dental period – Period after birth during which the neonate does not have any teeth. It lasts for 6 months after birth. Gum Pads The alveolar processes at the time of birth are known as gum pads. Gum pads are pink, firm and are covered by a dense layer of fibrous periosteum. They are horse-shoe-shaped and develop in 2 parts.
- 10. They are the labio-buccal portion and the lingual portion. The two portions of the gum pads are separated from each other by a groove called the Dental groove.The gum pads are divided into 10 segments by certain grooves called the teansverse grooves. Each of these segments consists of one developing deciduous tooth sac.
- 11. The gingival groove separates the gum pad from the palate and floor of the mouth. The transverse groove between the canine and first dec. molar segment is called the lateral sulcus. The lateral sulcus of the mandibular arch is normally more distal to that of the maxillary arch. The upper and lower gum pads are almost similar to each other. The upper pad is wider and longer than the mandibular. Thus, when the upper and lower gum pads are approximated, there is a complete overjet. Contact occurs between the upper and lower gum pads in first molar region and space exists between them in the anterior region. This infantile open bite is considered normal and helps in suckling.
- 12. Status Of Dentition The neonate is without teeth for 6 months of life. At birth the gum pads are not sufficiently wide to accommodate the developing incisors which are crowded in their crypts. During the first year of life the gum pads grow rapidly permitting the incisors to erupt in good alignment. Very rarely teeth are found to have erupted at the time of birth. Teeth that are present at the time of birth are called Natal teeth. Sometimes teeth eruptin an early stage. Teeth that erupt during the first month of age are called the Neonatal teeth. The natal and neonatal teeth are mostly located in mandibular incisor region and show a familial tendency.
- 13. 2. Deciduous Dentition Period – the The initiation of primary tooth buds occurs during the first 6 weeks of intra-uterine life. The primary teeth begin to erupt at about 6 months. The eruption of all primary teeth is completed by 2.5-3.5 years of age when the second dec. molars come into occlusion. Eruption Age And Sequence Of Deciduous Dentition The mand. central incisors are the first teeth to erupt into the oral cavity around 6-7 months of age. The timing of tooth eruption is highly variable. A 3 month variation is considered normal. The sequence of eruption of the dec. dentition is : A-B-D-C-E. The primary dentition is established by 3 years of age on eruption of the second dec. molars. Between 3-6 years of age, the dental arch is relatively stable and very few changes occur.
- 15. Spacing Of Deciduous Dentition Spacing exists between dec. teeth. These spaces are called as the physiological spaces or the developmental spaces. Spaces in dec. dentition is important for normal development of permanent dentition. Absence of spaces in dec. dentition is indicative of crowding in permanent dentition. Spacing is seen mesial to max. canines and distal to mand. Canines. These physiological spaces are called as the Primate spaces or Simian spaces or Anthropoid spaces.
- 16. Flush Terminal Plane The mesio-distal relation between the distal surfaces of the upper and lower dec. molars is called the terminal plane. A normal feature of dec. dentition is to find a flush terminal plane where the distal surfaces of the upper and lower second dec. molars are in the same vertical plane. Deep Bite A deep bite may occur in the initial stages of development. Deep bite is increased by the fact that the dec. incisors are more upright and the lower incisal edges often contact the cingulum area of the max. incisors. This deep bite is later reduced due to – eruption of dec. molars, attrition of incisors and forward movement of the mandible due to growth.
- 17. 3. Mixed-Dentition period – This period begins around 6 years of age with the eruption of the first per. Molars. Dec. teeth and some per. Teeth are present during this period. This period can be classified into 3 phases – 1) First Transitional period 2) Inter-Transitional period and 3) Second Transitional period. 1) First Transitional period – is characterized by the emergence of the first per. Molars and exchange of dec. incisors with the per. Incisors. Emergence of the First permanent molars The mandibular first molar is the first tooth to erupt at around 6 yrs of age. The first permanent molars are guided into the dental arch by the distal surface of the second dec. molars.
- 18. The mesio-distal relation between the distal surfaces of the upper and lower second dec. molars can be of three types - 1) Flush Terminal plane 2) Mesial Step Terminal plane 3) Distal Step Terminal plane
- 19. 1) Flush Terminal Plane – The distal surface of the upper and lower second dec. molars are in one vertical plane. This is called flush or vertical terminal plane. This is a normal feature of the dec. dentition. For the transition of such an end on molar relation to a Class I molar relation, the lower molar has to move forward by 3-5 mm relative to the upper molar. This occurs by utilization of the physiologic spaces and Leeway space in the lower arch and by differential forward growth of the mandible. The shift in lower molar from a flush terminal plane to a Class I relation can occur in two ways – a) Early Shift b) Late Shift. a) Early Shift – This occurs during the early mixed dentition period. The eruptive force of the first permanent molar is sufficient to push the dec. first and second molars forward in the arch to close the primate space and to establish a Class I molar relationship. As this occurs in the early mixed dentition period, it is called early shift.
- 20. 2) Mesial Step Terminal Plane – The distal surface of the lower second dec. molar is more mesial than that of the upper. Thus, the permanent molars erupt directly into Angle’s class I occlusion. This usually occurs due to early forward growth of the mandible. 3) Distal Step Terminal Plane – The distal surface of the lower second dec. molar is more distal to that of the upper. Thus the erupting per. Molars maybe in Angle’s Class II occlusion. b) Late Shift – Many children lack the primate space and the erupting permanent molars are unable to move forward to establish class I relationship. In these cases, when the dec. second molars exfoliate, the per. First molars drift mesially utilizing the Leeway space. This occurs in the late mixed dentition period and is thus called late shift.
- 21. The Exchange Of Incisors During the first transitional period the dec. incisors are replaced by the per. incisors The man. Per. incisors are the first to erupt. The per. incisors are considerably larger than the dec. teeth they replace. This difference between the amount of space needed for the accomodation of the incisors and the amount of space available for this is called ‘incisal liability’. This is roughly 7 mm in max. arch and 5 mm in man. arch. The incisal liability is overcome by the following factors – a) Utilization of interdental spaces seen in primary dentition b) Increase in inter-canine width c) Change in incisor inclination Inter-transitional Period In this period, the max. & man. arches consist of sets of dec. & per. Teeth. This phase is relatively stable and no change occurs.
- 22. The Second Transitional Period This period is characterized by the replacement of the dec. molars and canines by the premolars and per. cuspids. The combined mesio-distal width of the per. Canines and premolars is usually less than that of the dec. canines and molars. The surplus space is called ‘Leeway Space of Nance’. It is greater in the mand. Arch [1.8 mm] than the max. arch [3.4 mm]. The excess space available after the exchange of the dec. molars and canines is utilized for mesial frift of the man. Molars to establish Class I molar relation.
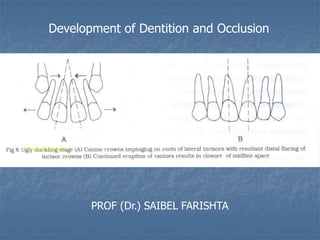
- 23. The Ugly Duckling Stage [Broadbent] This condition is sometimes seen during the eruption of per. Canines. As the developing per. Canines erupt, they displace the roots of the lateral incisors mesially. This results in transmitting of the force onto the roots of the central incisors which also get displaced mesially. A resultant distal divergence of the crowns of the two central incisors causes a midline spacing. This condition usually corrects by itself when canines erupt and the pressure is transferred from the roots to the coronal area of the incisors.
- 24. The Permanent Dentition Period The eruption sequence of the max. permanent dentition – 6 – 1 – 2 – 4 – 3 – 5 – 7 or 6 – 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 7 The eruption sequence of the man. permanent dentition – 6 – 1 – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 7 or 6 – 1 – 2 – 4 – 3 – 5 – 7
- 25. THANK YOU